Difference between revisions of "Advantech Robotic Suite/Time Sync Viewer"
From ESS-WIKI
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
* Multi-Sensor Timestamps Visualization: Visually displays the timestamps of multiple sensors to help users check data alignment. | * Multi-Sensor Timestamps Visualization: Visually displays the timestamps of multiple sensors to help users check data alignment. | ||
* Time Synchronization Flag (sync_flag): Automatically triggers a flag when synchronization conditions are met, providing instant confirmation. | * Time Synchronization Flag (sync_flag): Automatically triggers a flag when synchronization conditions are met, providing instant confirmation. | ||
| − | * Statistical Analysis: Calculates synchronization frequency, average time intervals, standard deviation, and other metrics to quantify performance. | + | <!--* Statistical Analysis: Calculates synchronization frequency, average time intervals, standard deviation, and other metrics to quantify performance.--> |
* Sensor Check: Assists users in identifying hardware delays, network jitter, and data loss that may result in incomplete data. | * Sensor Check: Assists users in identifying hardware delays, network jitter, and data loss that may result in incomplete data. | ||
* Improved Sensor Fusion: Enhances data consistency and stability for applications such as SLAM, robotic arms, drones, and AMRs. | * Improved Sensor Fusion: Enhances data consistency and stability for applications such as SLAM, robotic arms, drones, and AMRs. | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
#* The image displays multiple sync points, indicating that at those moments, the sensor data is properly synchronized. | #* The image displays multiple sync points, indicating that at those moments, the sensor data is properly synchronized. | ||
[[File:ROS2_time_sync_viewer_3.png|1000px|ROS2_time_sync_viewer]] | [[File:ROS2_time_sync_viewer_3.png|1000px|ROS2_time_sync_viewer]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
= How to = | = How to = | ||
| Line 77: | Line 58: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- | ||
| + | == Synchronization Statistics == | ||
| + | It provides detailed time synchronization statistics, including the Monitoring Metrics Description: | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Metric !! Description | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Sync Frequency || The number of times synchronized_callback is triggered per second (Hz). | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Avg Interval || The average time interval between each callback (seconds). | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Std Dev || The standard deviation of time intervals (seconds), indicating variability. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Max Interval || The maximum time interval, showing the longest delay. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Min Interval || The minimum time interval, showing the shortest synchronization time. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Monitoring results will be shown in the terminal | ||
| + | [[File:ROS2_time_sync_check_node_setting_2.png|none|ROS2_time_sync_check_node_setting_2]] | ||
| + | --> | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
Revision as of 04:35, 13 June 2025
Introduction
Time Sync Viewer is a time synchronization detection tool specifically designed for ROS2, provided as an rqt plugin. It is used to monitor and analyze the synchronization status of multi-sensor data in real time. In robotics applications, ensuring accurate time synchronization is crucial, as it directly affects the performance and stability of technologies such as SLAM, deep learning, and sensor fusion. Time Sync Viewer provides synchronization detection, visual analysis, and detailed time statistics, helping developers quickly identify and resolve synchronization issues.
Features and Advantages:
- Multi-Sensor Timestamps Visualization: Visually displays the timestamps of multiple sensors to help users check data alignment.
- Time Synchronization Flag (sync_flag): Automatically triggers a flag when synchronization conditions are met, providing instant confirmation.
- Sensor Check: Assists users in identifying hardware delays, network jitter, and data loss that may result in incomplete data.
- Improved Sensor Fusion: Enhances data consistency and stability for applications such as SLAM, robotic arms, drones, and AMRs.
Note: Time Sync Viewer is only supported on Ubuntu 22.04
GUI Description
Example Using Camera, IMU, and LiDAR
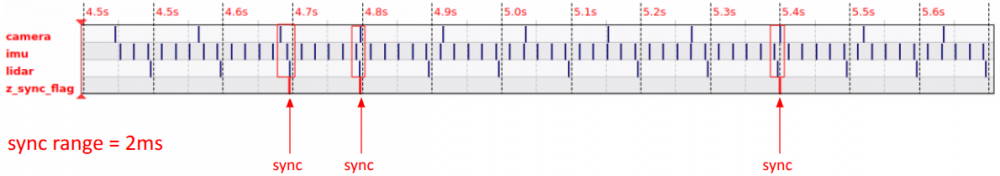
- Time Axis Display
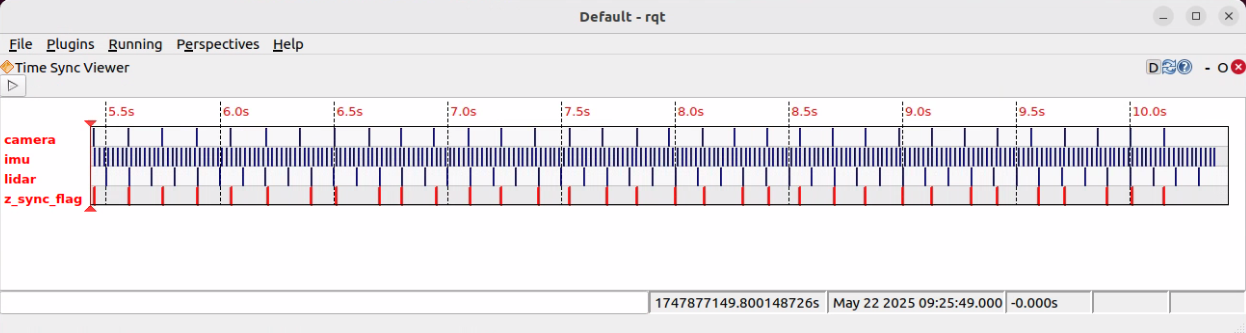
- The image displays the timestamps of different data streams (topics), where each horizontal line represents a topic. Examples include::
- camera (camera image)
- imu (IMU data)
- lidar (LiDAR scan)
- z_sync_flag (sync flag)
- The image displays the timestamps of different data streams (topics), where each horizontal line represents a topic. Examples include::
- Synchronization Range
- In this example, the
sync_rangeis configured with 2ms, meaning that data points arriving within this 2-millisecond window are considered synchronized. - On the time axis, when a synchronization event is triggered, a
sync_flagis marked.
- In this example, the
- Synchronization Analysis
- When all sensor data points fall within the 2ms range, they are considered synchronized (sync).
- The image displays multiple sync points, indicating that at those moments, the sensor data is properly synchronized.
How to
- Step 1: Publish fake sensor data, including camera, IMU, and LiDAR(you can also use actual sensors)
- In terminal 1, publish camera topic
-
cd /usr/local/Advantech/ros/humble/ros2-timesync-viewer/test/fake_sensor python3 camera.py - In terminal 2, publish lidar topic
-
cd /usr/local/Advantech/ros/humble/ros2-timesync-viewer/test/fake_sensor python3 lidar.py - In terminal 3, publish imu topic
-
cd /usr/local/Advantech/ros/humble/ros2-timesync-viewer/test/fake_sensor python3 imu.py
- Step 2: Run Time Sync Viewer in Web UI, select "Utility" from the list on the left
- Step 3: Set
Sync Periodto a value between 1ms and 2000ms (default: 100ms)
- Step 4: Click launch button, then will open
Time Sync Viewerwindow
- Step 5: Click start button
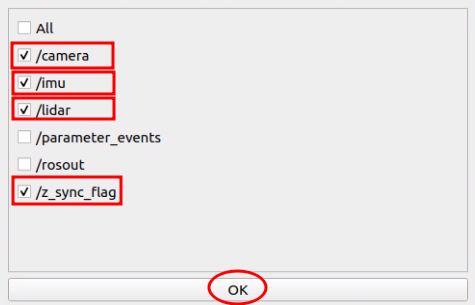
- Step 6: Select the topics that you want to view, then click OK
- Result: