Difference between revisions of "IoTGateway/BSP/Android/Gettingstarted/How to use UART"
Yuming.lin (talk | contribs) |
Yuming.lin (talk | contribs) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | = <span style="color: rgb(0, 0, 205);">'''<span style="font-size: large;">Overview</span>'''</span> = | |
| − | <span lang="en | + | <span lang="en"><font color="#000000">The Android/Linux UART/serial port access from user is through the tty-devices. The tty-devices have different names depending on UART driver on different board.</font></span> |
| − | <span lang="en"><font color="#000000">The utility stty can configure the serial speed. Then the com port can be accessed as a file:</font></span> Check baudrate | + | = <br/><span style="color: rgb(0, 0, 205);"><span style="font-size: large;">'''Configuration'''</span></span> = |
| + | |||
| + | == <span style="font-size: medium;"><font color="#0066cc">standard baud rate</font></span> == | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span lang="en"><font color="#000000">The utility stty can configure the serial speed. Then the com port can be accessed as a file:</font></span> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Check baudrate | ||
# stty -F /dev/ttymxc1 115200 | # stty -F /dev/ttymxc1 115200 | ||
| Line 15: | Line 21: | ||
#echo test > /dev/ttymxc1 | #echo test > /dev/ttymxc1 | ||
| − | + | == <span style="font-size: medium;"><font color="#0066cc">Change COM mode</font></span> == | |
| + | |||
| + | The COM port need to change mode for user space (APK). your can add the chmod cammand in the android init.rc file in device/fsl/rom_3420_a1/. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ex: chmod 666 /dev/ttymxc* | ||
| + | |||
| + | == <span style="font-size: medium;"><font color="#0066cc">RS-485</font></span> == | ||
| + | |||
| + | RS-485 uses half-duplex communication, which means that one medium is shared for transmitting and receiving data. Therefore the system needs to control the RS-485 transceiver's transmit mode. Usually the UART RTS signal is used to switch the transmitter on and off. Our modules provide the following support: | ||
| − | + | Enable the RS-485 feature by either using ioctrl ''TIOCSRS485'' from user space as described in [https://github.com/ADVANTECH-Corp/linux-imx6/blob/imx_4.1.15_1.0.0_ga/Documentation/serial/serial-rs485.txt <font color="#0066cc">RS-485 Kernel Documentation</font>]. | |
| − | + | | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | = '''<span style="font-size: large;"><span style="color: rgb(0, 0, 205);">Boards</span></span>''' = | |
| − | |||
| − | + | == ROM3420 Borad == | |
| − | |||
| − | + | {| style="width: 500px;" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" border="1" align="left" | |
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | '''COM Name''' | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | '''NXP/Freescale Name''' | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | '''Device''' | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | | ||
'''RS485 support''' | '''RS485 support''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | COM0 |
| − | COM0 | + | | UART2 |
| − | + | | | |
| − | | | ||
| − | UART2 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
/dev/ttymxc1 | /dev/ttymxc1 | ||
| − | + | | | |
Yes | Yes | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | COM1 |
| − | COM1 | + | | UART4 |
| − | + | | | |
| − | | | ||
| − | UART4 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
/dev/ttymxc3 | /dev/ttymxc3 | ||
| − | + | | | |
Yes | Yes | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | COM2 |
| − | COM2 | + | | UART5 |
| − | + | | | |
| − | | | ||
| − | UART5 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
/dev/ttymxc4 | /dev/ttymxc4 | ||
| − | + | | | |
Yes | Yes | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ROM3420 COM.png|252x213px|ROM3420 COM.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == ROM7421 Borad == | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| style="width: 500px;" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" border="1" align="left" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | '''COM Name''' | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | '''NXP/Freescale Name''' | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | '''Device''' | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | | ||
'''RS485 support''' | '''RS485 support''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | COM0 |
| − | COM0 | + | | UART2 |
| − | + | | | |
| − | | | ||
| − | UART2 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
/dev/ttymxc1 | /dev/ttymxc1 | ||
| − | + | | | |
No | No | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | COM1 |
| − | COM1 | + | | UART4 |
| − | + | | | |
| − | | | ||
| − | UART4 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
/dev/ttymxc3 | /dev/ttymxc3 | ||
| − | + | | | |
No | No | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | = <span style="color: rgb(0, 0, 205);"><span style="font-size: large;">'''Test Sample'''</span></span> = | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1. Click "Serial Port" | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Imx6ABV1 APP serialport.png|972x187px|Imx6ABV1 APP serialport.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2. Click "Setup" | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Imx6ABV1 serialport setup.png|973x552px|Imx6ABV1 serialport setup.png]] | ||
| + | |||
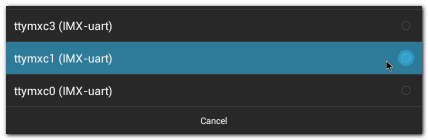
| + | 3. Click "Device" , and choose the used device(e.g. ttymxc1) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Imx6ABV1 serialport setup device 1.png|492x140px|Imx6ABV1 serialport setup device 1.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4. Click "Baud rate" , and choose the used baudrate(e.g. 115200) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Imx6ABV1 serialport setup device 2.png|428x140px|Imx6ABV1 serialport setup device 2.png]] | ||
Latest revision as of 07:39, 6 February 2017
Contents
Overview
The Android/Linux UART/serial port access from user is through the tty-devices. The tty-devices have different names depending on UART driver on different board.
Configuration
standard baud rate
The utility stty can configure the serial speed. Then the com port can be accessed as a file:
Check baudrate
# stty -F /dev/ttymxc1 115200
Read
#cat /dev/ttymxc1 &
Send
#echo test > /dev/ttymxc1
Change COM mode
The COM port need to change mode for user space (APK). your can add the chmod cammand in the android init.rc file in device/fsl/rom_3420_a1/.
ex: chmod 666 /dev/ttymxc*
RS-485
RS-485 uses half-duplex communication, which means that one medium is shared for transmitting and receiving data. Therefore the system needs to control the RS-485 transceiver's transmit mode. Usually the UART RTS signal is used to switch the transmitter on and off. Our modules provide the following support:
Enable the RS-485 feature by either using ioctrl TIOCSRS485 from user space as described in RS-485 Kernel Documentation.
Boards
ROM3420 Borad
| COM Name | NXP/Freescale Name | Device |
RS485 support |
|---|---|---|---|
| COM0 | UART2 |
/dev/ttymxc1 |
Yes |
| COM1 | UART4 |
/dev/ttymxc3 |
Yes |
| COM2 | UART5 |
/dev/ttymxc4 |
Yes |
ROM7421 Borad
| COM Name | NXP/Freescale Name | Device |
RS485 support |
|---|---|---|---|
| COM0 | UART2 |
/dev/ttymxc1 |
No |
| COM1 | UART4 |
/dev/ttymxc3 |
No |
Test Sample
1. Click "Serial Port"
2. Click "Setup"
3. Click "Device" , and choose the used device(e.g. ttymxc1)
4. Click "Baud rate" , and choose the used baudrate(e.g. 115200)