Difference between revisions of "Advantech Robotic Suite/DeviceOn"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | |||
= Introduction = | = Introduction = | ||
| − | + | Robotic applications often require remote management for various reasons. Here are some key reasons why remote management is important for robotic applications: | |
| + | |||
| + | Accessibility and Monitoring: Remote management allows operators, developers, or administrators to access and monitor robotic systems from a remote location. This is particularly useful when the robots are deployed in remote or hazardous environments where direct physical access might be difficult or unsafe. Remote management enables real-time monitoring of robot status, sensor data, and overall system performance. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Configuration and Software Updates: Remote management facilitates the configuration and software updates of robotic systems. It allows administrators to remotely modify parameters, settings, or behavior of robots without the need for physical intervention. This flexibility is crucial for adjusting robot behavior, optimizing performance, or adapting to changing operational requirements. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Diagnostics and Troubleshooting: Remote management enables remote diagnostics and troubleshooting of robotic systems. Operators or developers can remotely access robot logs, sensor data, and other diagnostic information to identify issues or errors. They can then analyze the data and perform necessary debugging or maintenance tasks without being physically present with the robot. | ||
| − | + | Remote Control and Teleoperation: Remote management enables remote control and teleoperation of robots. Operators can remotely manipulate the robot's movements, perform tasks, or respond to dynamic situations. This is especially useful for scenarios where human intervention or decision-making is required, such as in disaster response, exploration, or complex manufacturing processes. | |
| − | + | Collaboration and Expert Assistance: Remote management facilitates collaboration and expert assistance in robotic applications. It allows multiple stakeholders, including experts, researchers, or operators, to remotely collaborate and provide guidance or support for complex robot operations. Experts can remotely access robot systems to provide troubleshooting, training, or knowledge transfer, thereby improving overall efficiency and effectiveness. | |
| − | + | Overall, remote management plays a vital role in robotic applications by providing accessibility, monitoring, configuration, diagnostics, control, and collaboration capabilities from remote locations. It enhances the flexibility, efficiency, and safety of robotic systems, making them more adaptable to various operational scenarios and enabling human-robot interaction over distances. | |
| | ||
Revision as of 03:38, 2 June 2023
Contents
Introduction
Robotic applications often require remote management for various reasons. Here are some key reasons why remote management is important for robotic applications:
Accessibility and Monitoring: Remote management allows operators, developers, or administrators to access and monitor robotic systems from a remote location. This is particularly useful when the robots are deployed in remote or hazardous environments where direct physical access might be difficult or unsafe. Remote management enables real-time monitoring of robot status, sensor data, and overall system performance.
Configuration and Software Updates: Remote management facilitates the configuration and software updates of robotic systems. It allows administrators to remotely modify parameters, settings, or behavior of robots without the need for physical intervention. This flexibility is crucial for adjusting robot behavior, optimizing performance, or adapting to changing operational requirements.
Diagnostics and Troubleshooting: Remote management enables remote diagnostics and troubleshooting of robotic systems. Operators or developers can remotely access robot logs, sensor data, and other diagnostic information to identify issues or errors. They can then analyze the data and perform necessary debugging or maintenance tasks without being physically present with the robot.
Remote Control and Teleoperation: Remote management enables remote control and teleoperation of robots. Operators can remotely manipulate the robot's movements, perform tasks, or respond to dynamic situations. This is especially useful for scenarios where human intervention or decision-making is required, such as in disaster response, exploration, or complex manufacturing processes.
Collaboration and Expert Assistance: Remote management facilitates collaboration and expert assistance in robotic applications. It allows multiple stakeholders, including experts, researchers, or operators, to remotely collaborate and provide guidance or support for complex robot operations. Experts can remotely access robot systems to provide troubleshooting, training, or knowledge transfer, thereby improving overall efficiency and effectiveness.
Overall, remote management plays a vital role in robotic applications by providing accessibility, monitoring, configuration, diagnostics, control, and collaboration capabilities from remote locations. It enhances the flexibility, efficiency, and safety of robotic systems, making them more adaptable to various operational scenarios and enabling human-robot interaction over distances.
DeviceOn
A surge in market demand for Industrial IoT products has rapidly increased the number of connected devices that are currently deployed and managed across different locations. It is essential to effectively manage, monitor, and control thousands of connected devices while ensuring uninterrupted service. Devices must work properly and securely after they have been deployed - w.
More information please refer to DeviceOn
Device Management
After your device onboarding, you could view, edit device basic information, remote control, and retrieve sensor data on your devices. Nine sub items under Device, Device List contain device name, upgrade status, power management and etc. Device Monitoring to give device loading at present. To remote diagnostic and debug through Remote Control. Next, all of plugin sensor data from Device Data. To grouping your device through the Device Group. For batch real-time or schedule control through Task defined. Rule Engine to set a threshold rule for your devices data in real-time.
Container Management
DeviceOn support Container Management function for you to deploy, monitor, and manage each container on different devices. You can manage and monitor the health of containers within minutes. Container Management function also provide a variety of container restart strategies for you to set the restart policy. Through the dashboard, you can quickly understand the running status of the container in the managed device. In addition, for container developers.
Azure Container Repository allows you to build, store, and manage container images and artifacts in a private registry for all types of container deployments. Use Azure container registries with your existing container development and deployment pipelines. Azure Container Registry is supported as a public cloud solution in the DeviceOn and support Harbor as a private cloud container repository. For more detailed information and operation steps, please refer to DeviceOn Manual - Container Management Section .
ROS 2 nodes can be running in Docker containers, it offers several benefits:
Isolation
Docker containers provide robust isolation, allowing each node to run in a separate environment. This prevents interference between nodes, which is particularly important in ROS, where nodes can be software components from different teams or developers. Container isolation ensures their independence.
Portability
Docker containers offer platform independence, meaning you can run the same ROS 2 nodes on different operating systems (e.g., Linux, Windows, macOS) and hardware platforms without worrying about dependencies and environment configurations. This makes deploying and running ROS 2 nodes in different environments much easier.
Easy Deployment
Using Docker containers simplifies the deployment process of ROS 2 nodes. You can package the nodes along with their dependencies and configurations into a Docker image and run it in any Docker-supported environment. This eliminates the hassle of dependency installations and configurations while ensuring node consistency across different environments.
Scalability
Docker containers provide lightweight and scalable deployment solutions. You can run multiple instances of the same or different ROS 2 node containers and manage them using container orchestration tools like Docker Compose or Kubernetes. This makes running ROS 2 nodes in distributed systems easier and allows dynamic adjustment of the number and configuration of nodes based on demand.
In summary, running ROS 2 nodes in Docker containers offers benefits such as isolation, portability, easy deployment, and scalability. These advantages make it convenient and flexible to develop, test, and deploy ROS 2 applications in different environments.
How to
In this section, we will instrduct you how to register a new account form DeviceOn trial portal and setup your edge device to connect to DeviceOn trial portal. After your edge device is managed in DeviceOn trial portal, you can find it is listed in the DeviceOn Device List, you can easily monitor it's status and deploy ROS2 node into it.
Register to DeviceOn Trial Portal
- DeviceOn Trial Portal: https://deviceon-trial.wise-paas.com/
- Login ID & password: <Follow below steps to register a new account>
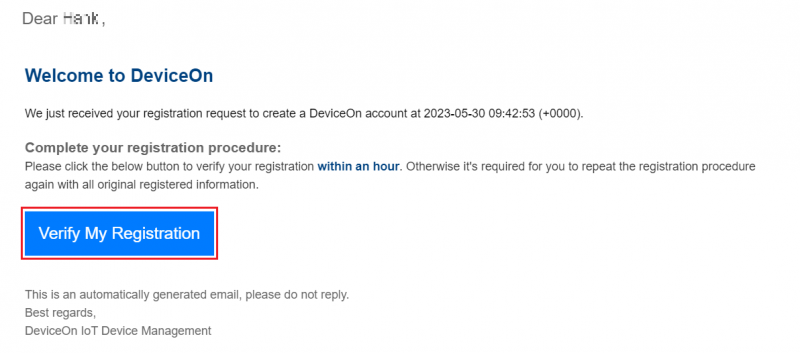
Step1. Register a new account from DeviceOn Trial Protal.
Step2. Verify account from DeviceOn Account Registration e-mail.
Setup WISE-Agent
Step1. Login DeviceOn Trial Portal.
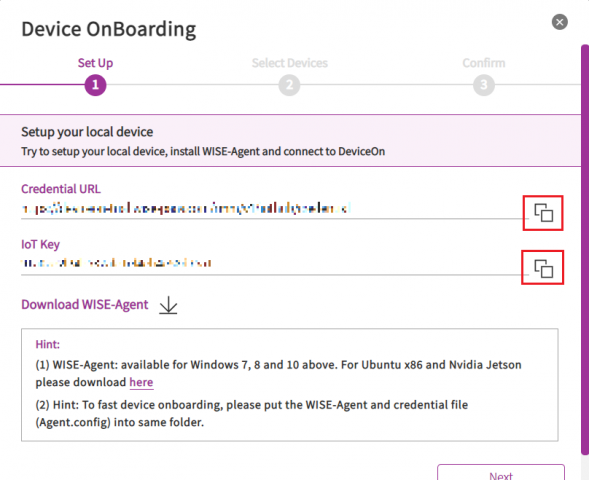
Step2. Click on Add device icon, you can find Credential URL and IoT Key are list in this page. you will be prompt to input these two strings in the following WISE-Agent setup steps.
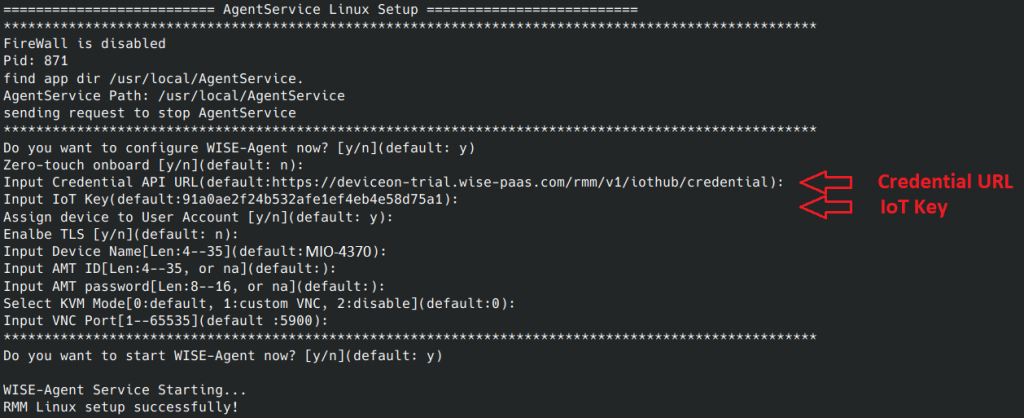
Step3. Launch WISE Agent setup program.
Step4. Copy Credential URL from DeviceOn Trial portal and paste it to the WISE Agent setup program while it is prompt to input.
Step5. Copy IoT Key from DeviceOn Trial portal and paste it to the WISE Agent setup program while it is prompt to input.
Step6. Finish the setup with default settings, then WISE-Agent Service will restart to connect to DeviceOn trial portal.
(You can refer to Edge Installation & Onboarding to get for detail description about install WISE-Agent and setup WISE-Agent for connecting to DeviceOn.)
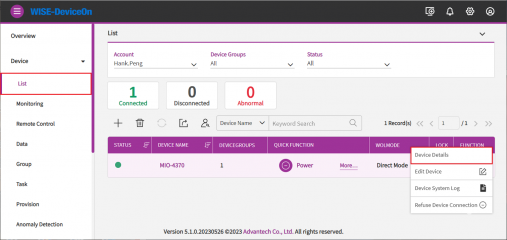
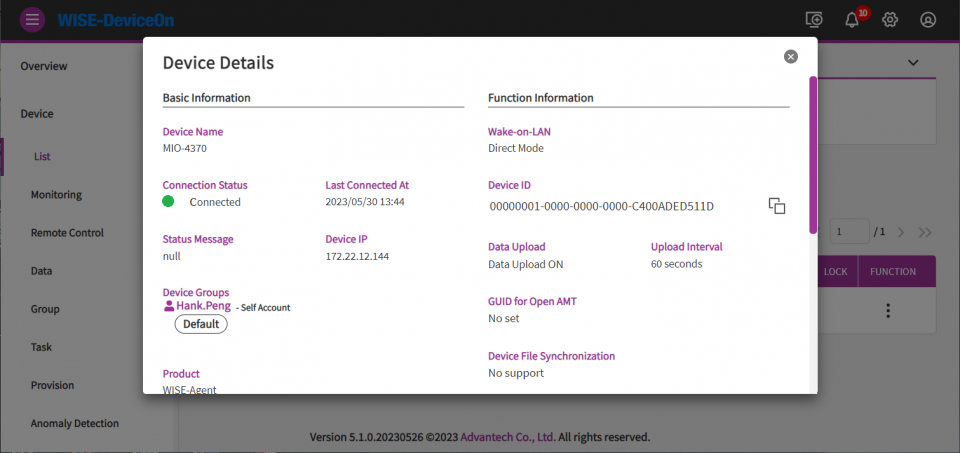
From "Device List" table, click on device name or device details to get device information.
You could get the device detail information such as, device IP, version, MAC, Memory, BIOS, operation system in this page.
Container Registry Configuration
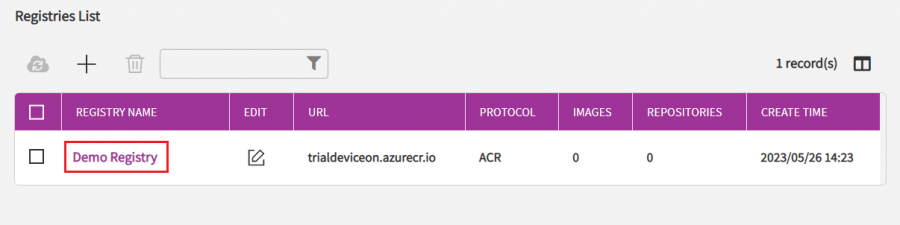
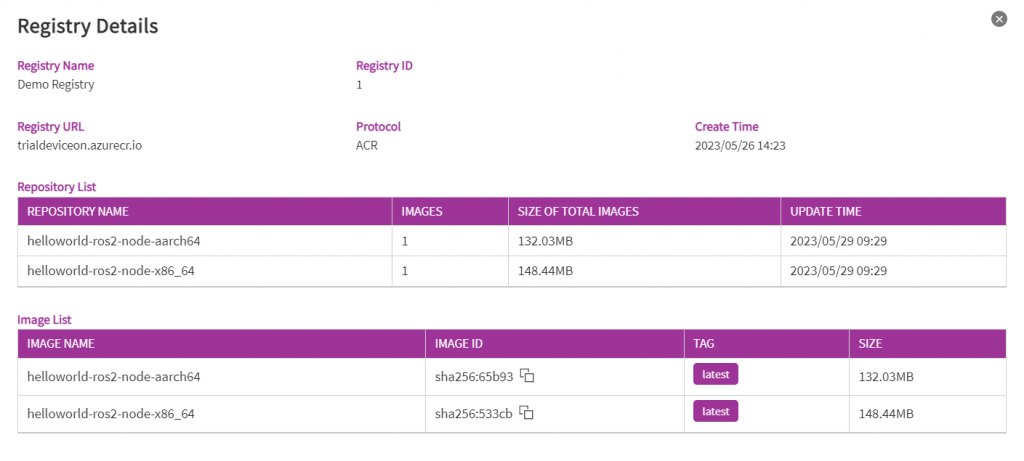
Helloworld ROS2 node is a sample ROS2 container and is already pre-upload to the DeviceOn Container Registry. You can find it in the Registry Detail page of "Demo Registry".
Click on the registry name "Demo Registry", you can see how many containers in the container registry are available for you to deploy.
ROS2 Node Deployment
Below steps will introduce you to deploy a ROS2 container to your edge device.
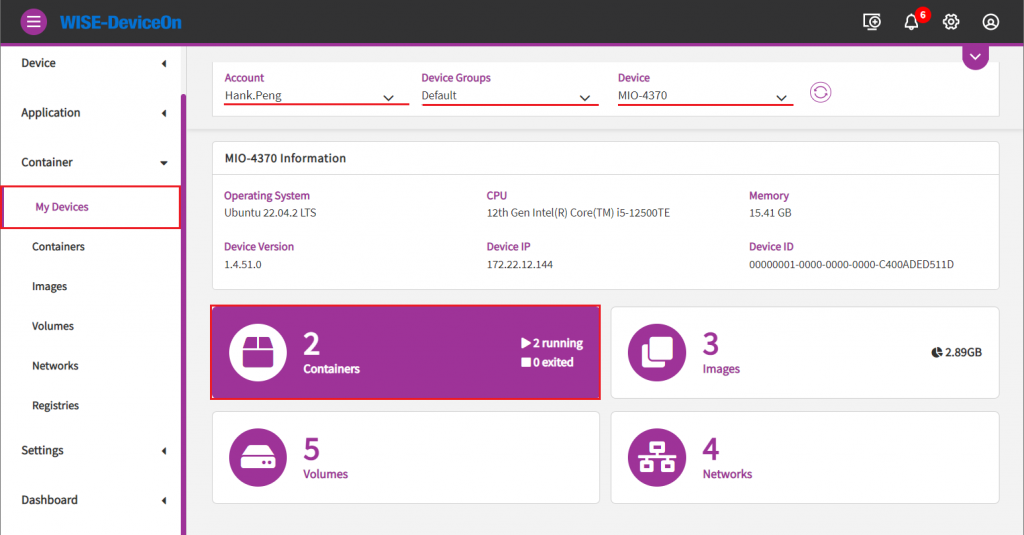
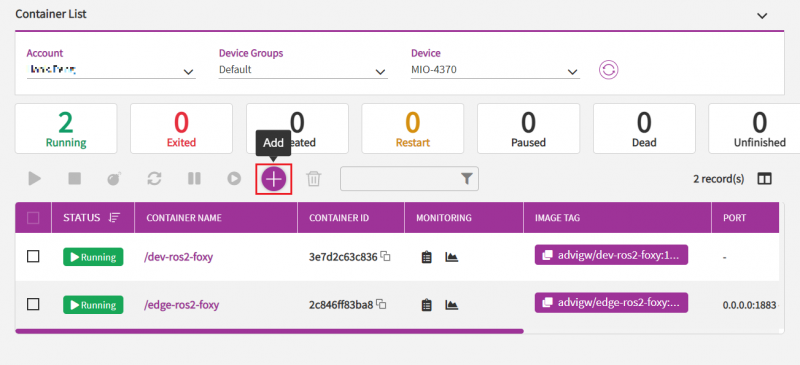
Step1. From left side bar, open "My Devices" page from "Container" function and then:
- Choose your device group.
- Choose your device from your device group.
- Click on Containers icon to see container list in this device.
Step2. Click "Add" icon to go into add container page.
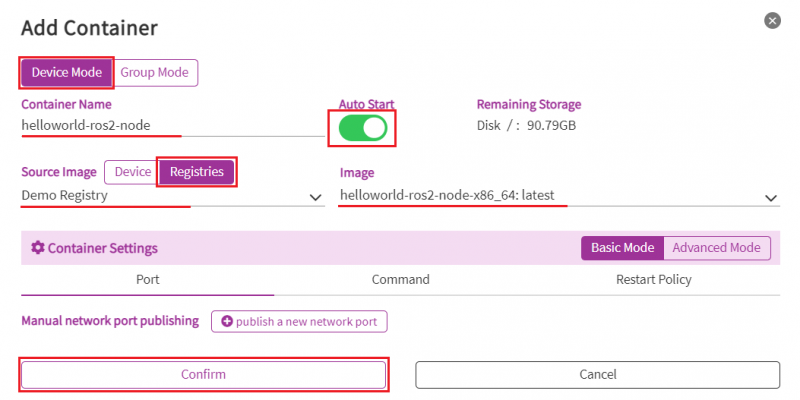
Step3. In the "Add Container" page, select parameters like below:
- Mode: Device Mode
- Container Name: <Give a container name by yourdelf>.
- Auto Start: On
- Source Image: Registries
- Registry: Demo Registry
- Image: helloworld-ros2-node-<platform-architecture>
Note, if your device is a Intel x86_64 architecture , please choose "helloworld-ros2-node-x86_64". If your device is a ARM architecture, please choose "helloworld-ros2-node-aarch64".
Now, you can click "Confirm" to start deploy helloworld-ros2-node to your device.
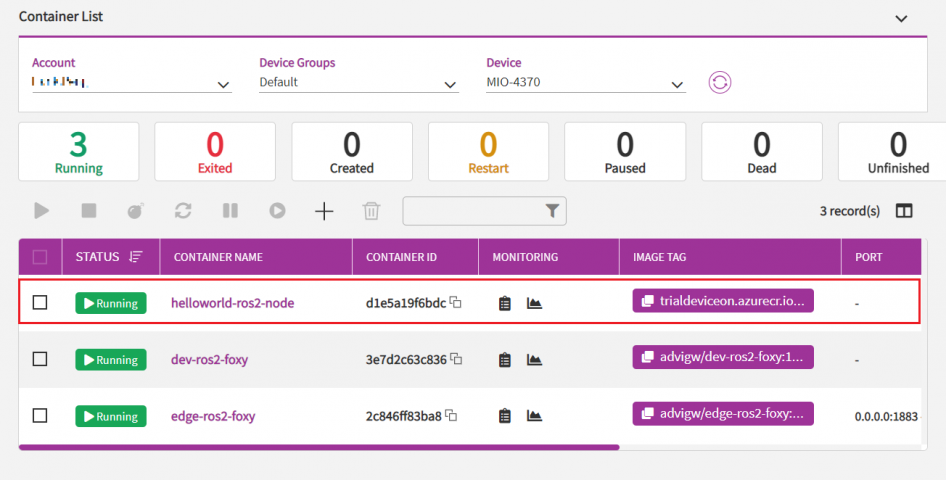
After several seconds, you can see the container is deployed into your device and status of helloworld-ros2-node is running.
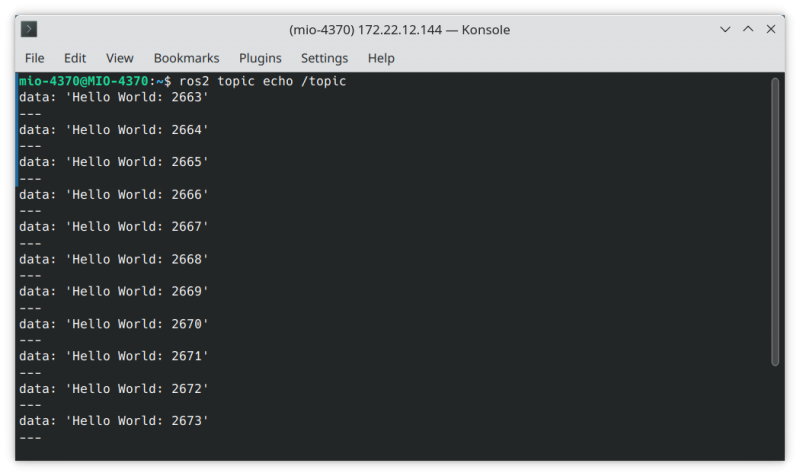
Step5. Now, helloworld-ros2-node is running and publishing "Hello World: <count>" message continuously, To subscribe the data that helloworld-ros2-node published, open a terminal from your device and execute below command:
1. Setup ROS2 environmant variables:
$ source /opt/ros/${ROS_DISTRO}/setup.bash
2. Subscribe the topic of helloworld node:
$ ros2 topic echo /topic
Result:
data: 'Hello World: 2663' --- data: 'Hello World: 2664' --- data: 'Hello World: 2665' --- data: 'Hello World: 2666' --- data: 'Hello World: 2667' --- data: 'Hello World: 2668' --- data: 'Hello World: 2669' ---