Difference between revisions of "Advantech Robotic Suite/Robotic System/AMR SDK"
From ESS-WIKI
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
= Software Stack = | = Software Stack = | ||
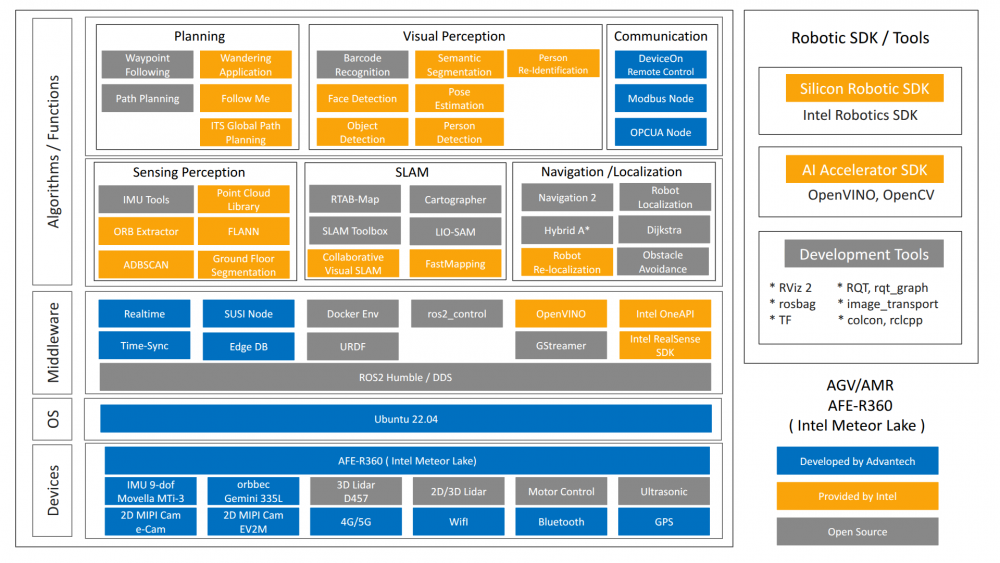
| − | The figure shows the overall software stack of the | + | The figure shows the overall software stack of the Advantech Robotic Suite for AFE-R360. |
| − | [[File:Robotic-suite-sw-stack-amr-01.png|center| | + | [[File:Robotic-suite-sw-stack-amr-01.png|center|1000px]] |
| − | = Planning = | + | = AMR SDK = |
| + | == Planning == | ||
<div style="overflow-x:auto;"> | <div style="overflow-x:auto;"> | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:90%;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:90%;" | ||
| Line 12: | Line 13: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Waypoint Following | | Waypoint Following | ||
| − | | | + | | A navigation approach where the robot is guided through a series of predefined locations (waypoints), ensuring it follows a specific path or route accurately. |
| http | | http | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Path Planning | | Path Planning | ||
| − | | | + | | A fundamental robotics technique that calculates an optimal or feasible path for a robot to move from a start point to a goal point while avoiding obstacles. |
| http | | http | ||
|} | |} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | = Visual Perception = | + | == Visual Perception == |
<div style="overflow-x:auto;"> | <div style="overflow-x:auto;"> | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:90%;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:90%;" | ||
| Line 34: | Line 35: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | = Sensing Perception = | + | == Sensing Perception == |
<div style="overflow-x:auto;"> | <div style="overflow-x:auto;"> | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:90%;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:90%;" | ||
| Line 42: | Line 43: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| IMU Tools | | IMU Tools | ||
| − | | | + | | A set of utilities for processing and visualizing data from Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs), which provide orientation, acceleration, and angular velocity information. |
| − | | | + | | [https://github.com/CCNYRoboticsLab/imu_tools Github] |
|} | |} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | = SLAM = | + | == SLAM == |
<div style="overflow-x:auto;"> | <div style="overflow-x:auto;"> | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:90%;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:90%;" | ||
| Line 55: | Line 56: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| RTAB-Map | | RTAB-Map | ||
| − | | | + | | Real-Time Appearance-Based Mapping (RTAB-Map) is a graph-based SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) algorithm that creates 3D maps using visual, depth, and sensor data. |
| − | | | + | | [https://github.com/introlab/rtabmap_ros Github] |
|- | |- | ||
| Cartographer | | Cartographer | ||
| − | | | + | | A real-time SLAM algorithm developed by Google that enables robots to build 2D and 3D maps of their environment using laser and odometry data. |
| − | | | + | | [https://google-cartographer-ros.readthedocs.io/en/latest/ Doc]<br>[https://github.com/ros2/cartographer_ros Github] |
|- | |- | ||
| SLAM Toolbox | | SLAM Toolbox | ||
| − | | | + | | A collection of SLAM algorithms and tools for lifelong mapping and localization, supporting online and offline map building, pose-graph optimization, and loop closure. |
| − | | | + | | [https://github.com/SteveMacenski/slam_toolbox Github] |
|- | |- | ||
| LIO-SAM | | LIO-SAM | ||
| − | | | + | | Lidar-Inertial Odometry via Smoothing and Mapping (LIO-SAM) is a state-of-the-art SLAM system that fuses LiDAR and IMU data to produce accurate, high-frequency odometry and maps. |
| − | | | + | | [https://github.com/TixiaoShan/LIO-SAM/tree/ros2 Github] |
|} | |} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | = Navigation /Localization = | + | == Navigation /Localization == |
<div style="overflow-x:auto;"> | <div style="overflow-x:auto;"> | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:90%;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:90%;" | ||
| Line 80: | Line 81: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Navigation 2 | | Navigation 2 | ||
| − | | | + | | A ROS 2 framework that provides a complete set of navigation features, including localization, path planning, and control, for autonomous robot movement in dynamic environments. |
| http | | http | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Robot Localization | | Robot Localization | ||
| − | | | + | | A ROS package that fuses data from various sensors (e.g., GPS, IMU, odometry) to provide accurate state estimation of a robot’s position and orientation. |
| http | | http | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Hybrid A* | | Hybrid A* | ||
| − | | | + | | An advanced path planning algorithm that combines the flexibility of A* search with continuous motion primitives, enabling smooth and feasible paths for wheeled robots. |
| http | | http | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Dijkstra | | Dijkstra | ||
| − | | | + | | A classic graph-based algorithm used for finding the shortest path between nodes, widely used in robotics for global path planning due to its completeness and optimality. |
| http | | http | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Obstacle Avoidance | | Obstacle Avoidance | ||
| − | | | + | | A core robotics capability where sensors and algorithms work together to detect and navigate around obstacles, ensuring safe and collision-free movement. |
| http | | http | ||
|} | |} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 08:47, 6 June 2025
Software Stack
The figure shows the overall software stack of the Advantech Robotic Suite for AFE-R360.
AMR SDK
Planning
| Application | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Waypoint Following | A navigation approach where the robot is guided through a series of predefined locations (waypoints), ensuring it follows a specific path or route accurately. | http |
| Path Planning | A fundamental robotics technique that calculates an optimal or feasible path for a robot to move from a start point to a goal point while avoiding obstacles. | http |
Visual Perception
| Application | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Barcode Recognition | Basic ROS 2 wrapper for the zbar barcode reader library. Reads image stream from image topic, and outputs detected barcodes to barcode topic. Works with 1D and 2D barcodes. | Github |
Sensing Perception
| Application | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| IMU Tools | A set of utilities for processing and visualizing data from Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs), which provide orientation, acceleration, and angular velocity information. | Github |
SLAM
| Application | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| RTAB-Map | Real-Time Appearance-Based Mapping (RTAB-Map) is a graph-based SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) algorithm that creates 3D maps using visual, depth, and sensor data. | Github |
| Cartographer | A real-time SLAM algorithm developed by Google that enables robots to build 2D and 3D maps of their environment using laser and odometry data. | Doc Github |
| SLAM Toolbox | A collection of SLAM algorithms and tools for lifelong mapping and localization, supporting online and offline map building, pose-graph optimization, and loop closure. | Github |
| LIO-SAM | Lidar-Inertial Odometry via Smoothing and Mapping (LIO-SAM) is a state-of-the-art SLAM system that fuses LiDAR and IMU data to produce accurate, high-frequency odometry and maps. | Github |
| Application | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Navigation 2 | A ROS 2 framework that provides a complete set of navigation features, including localization, path planning, and control, for autonomous robot movement in dynamic environments. | http |
| Robot Localization | A ROS package that fuses data from various sensors (e.g., GPS, IMU, odometry) to provide accurate state estimation of a robot’s position and orientation. | http |
| Hybrid A* | An advanced path planning algorithm that combines the flexibility of A* search with continuous motion primitives, enabling smooth and feasible paths for wheeled robots. | http |
| Dijkstra | A classic graph-based algorithm used for finding the shortest path between nodes, widely used in robotics for global path planning due to its completeness and optimality. | http |
| Obstacle Avoidance | A core robotics capability where sensors and algorithms work together to detect and navigate around obstacles, ensuring safe and collision-free movement. | http |