|
|
| (13 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| | {{DISPLAYTITLE:Android Peripheral Features}} | | {{DISPLAYTITLE:Android Peripheral Features}} |
| | | | |
| − | ==Backlight== | + | == Serial Port == |
| − | ===The relevant files===
| |
| − | /sys/class/graphics/fb0
| |
| − | /sys/devices/platform/mxc_sdc_fb.1/graphics/fb0
| |
| − | /sys/devices/platform/mxc_sdc_fb.1/graphics/fb0/power
| |
| − | /sys/devices/platform/mxc_sdc_fb.1
| |
| − | /sys/class/graphics
| |
| − | /sys/class/backlight
| |
| − | /sys/class/backlight/pwm-backlight.0
| |
| | | | |
| − | ===Turn off===
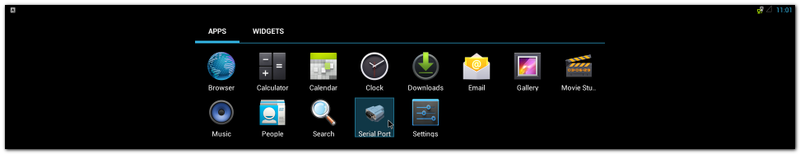
| + | #Click "Serial Port" |
| − | echo 1 > /sys/class/backlight/pwm-backlight.0/bl_power
| + | #:[[File:Imx6ABV1 APP serialport.png|800px|Imx6ABV1 APP serialport.png]] |
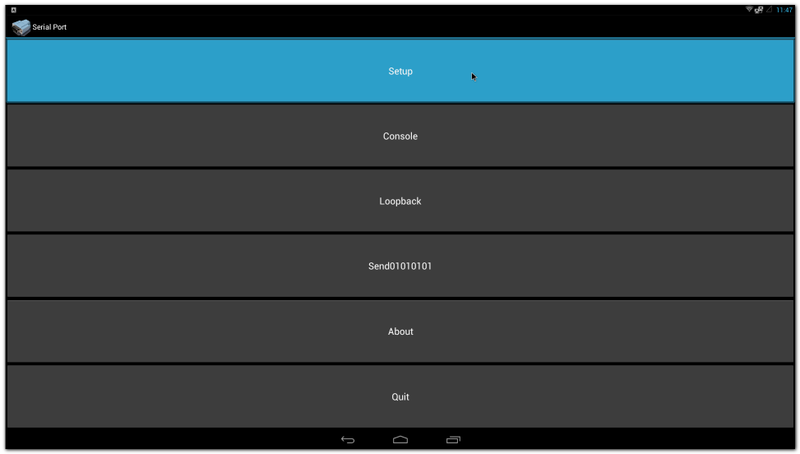
| | + | #Click "Setup" |
| | + | #:[[File:Imx6ABV1 serialport setup.png|800px|Imx6ABV1 serialport setup.png]] |
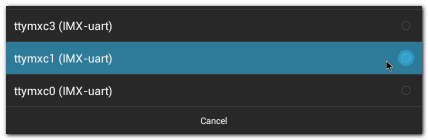
| | + | #Click "Device" , and choose the used device(e.g. ttymxc1) |
| | + | #:[[File:Imx6ABV1 serialport setup device 1.png|RTENOTITLE]] |
| | + | #Click "Baud rate" , and choose the used baudrate(e.g. 115200) |
| | + | #:[[File:Imx6ABV1 serialport setup device 2.png|RTENOTITLE]] |
| | | | |
| − | ===Turn on=== | + | == Wi-Fi == |
| − | echo 0 > /sys/class/backlight/pwm-backlight.0/bl_power
| |
| | | | |
| − | ===Brightness control===
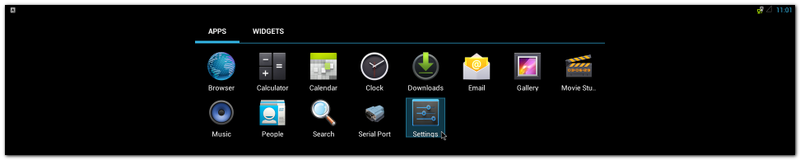
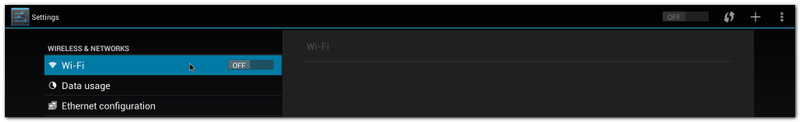
| + | #Click "Settings" |
| − | echo 0 > /sys/class/backlight/pwm-backlight.0/brightness
| + | #:[[File:Imx6ABV1 APP settings.png|800px|Imx6ABV1 APP settings.png]] |
| − | echo 255 > /sys/class/backlight/pwm-backlight.0/brightness
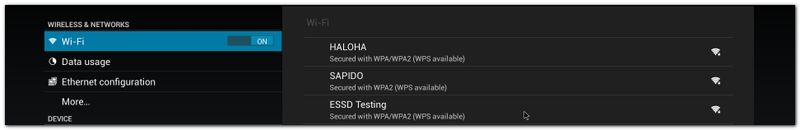
| + | #Turn Wi-Fi on |
| | + | #:[[File:Imx6ABV1 settings wifi on.png|800px|Imx6ABV1 settings wifi on.png]] |
| | + | #Choose ESSID (e.g. ESSD Testing ) |
| | + | #:[[File:Imx6ABV1 settings wifi choose ESSID.png|800px|Imx6ABV1 settings wifi choose ESSID.png]] |
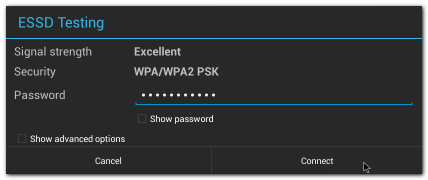
| | + | #Input correct password |
| | + | #:[[File:Imx6ABV1 settings wifi password.png|RTENOTITLE]] |
| | + | #Wi-Fi Authenticating/Connecting/Obtaining IP address |
| | + | #:[[File:Imx6ABV1 settings wifi authenticating.png|800px|Imx6ABV1 settings wifi authenticating.png]] |
| | + | #:[[File:Imx6ABV1 settings wifi connecting.png|800px|Imx6ABV1 settings wifi connecting.png]] |
| | + | #:[[File:Imx6ABV1 settings wifi obtaining ip.png|800px|Imx6ABV1 settings wifi obtaining ip.png]] |
| | + | #Wi-Fi connected |
| | + | #:[[File:Imx6ABV1 settings wifi connected.png|800px|Imx6ABV1 settings wifi connected.png]] |
| | | | |
| − | ==Camera==
| + | == Ethernet == |
| − | Example
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==CAN Bus==
| |
| − | ===Configuration/Testing===
| |
| − | ====Configuration====
| |
| − | *Connect can0 and can1
| |
| − | | |
| − | <CAN1_D+> connect to <CAN2_D+>
| |
| − | | |
| − | <CAN1_D-> connect to <CAN2_D->
| |
| − | | |
| − | # ip link set can0 up type can bitrate 125000
| |
| − | # ip link set can1 up type can bitrate 125000
| |
| − | | |
| − | ====Testing====
| |
| − | *Test 1
| |
| − | # candump can1 &
| |
| − | # cansend can0 12345678#123412341234
| |
| − | The following shows the result
| |
| − | can1 12345678 [6] 12 34 12 34 12 34
| |
| − | | |
| − | *Test 2
| |
| − | # cansend can0 133#ababdede
| |
| − | The following shows the result
| |
| − | can1 133 [4] AB AB DE DE
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==CPU==
| |
| − | ===CPU Frequency===
| |
| − | ;Using available CPU frequency policies
| |
| − | Read CPU frequency
| |
| − | # cpufreq-info | grep "current CPU frequency"
| |
| − | current CPU frequency is 396 MHz (asserted by call to hardware).
| |
| − | current CPU frequency is 396 MHz (asserted by call to hardware).
| |
| − | current CPU frequency is 396 MHz (asserted by call to hardware).
| |
| − | current CPU frequency is 396 MHz (asserted by call to hardware).
| |
| − | | |
| − | Check available CPU frequency policy
| |
| − | # cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_available_governors
| |
| − | conservative ondemand userspace powersave interactive performance
| |
| − | | |
| − | Change CPU frequency policy
| |
| − | # echo performance > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_governor
| |
| − | | |
| − | Check CPU frequency
| |
| − | # cpufreq-info | grep "current CPU frequency"
| |
| − | current CPU frequency is 996 MHz (asserted by call to hardware).
| |
| − | current CPU frequency is 996 MHz (asserted by call to hardware).
| |
| − | current CPU frequency is 996 MHz (asserted by call to hardware).
| |
| − | current CPU frequency is 996 MHz (asserted by call to hardware).
| |
| − | | |
| − | ;Setting the CPU frequency explicitly
| |
| − | Read available CPU frequenies
| |
| − | # cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_available_frequencies
| |
| − | 396000 792000 996000
| |
| − | | |
| − | Change CPU frequency explicitly
| |
| − | # echo userspace > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_governor
| |
| − | # echo 792000 > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_setspeed
| |
| − | | |
| − | Check CPU frequency
| |
| − | # cpufreq-info | grep "current CPU frequency"
| |
| − | current CPU frequency is 792 MHz (asserted by call to hardware).
| |
| − | current CPU frequency is 792 MHz (asserted by call to hardware).
| |
| − | current CPU frequency is 792 MHz (asserted by call to hardware).
| |
| − | current CPU frequency is 792 MHz (asserted by call to hardware).
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ===CPU Hot-Plugging===
| |
| − | Manually turn off CPU cores
| |
| − | #echo 0 > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu1/online
| |
| − | CPU1: shutdown
| |
| − | | |
| − | *Can't turn off cpu0
| |
| − | | |
| − | Check CPU is turned off
| |
| − | #cat /proc/interrupts | head -n 1
| |
| − | CPU0 CPU2 CPU3
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==Ethernet== | |
| − | Example
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==Framebuffer==
| |
| − | Example
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==GPIO==
| |
| − | ===Configuration/Testing===
| |
| − | ====Configuration====
| |
| − | Export GPIO then you can use control GPIO from userr space through sysfs
| |
| − | | |
| − | GPIO 27 is taken as an example:
| |
| − | | |
| − | Export GPIO 27
| |
| − | # echo 27 /sys/class/gpio/export
| |
| − | | |
| − | Set GPIO direction to in/out
| |
| − | # echo "in" > /sys/class/gpio/gpio27/direction
| |
| − | | |
| − | Set GPIO value 0/1 if GPIO pin define is output
| |
| − | # echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio27/value
| |
| − | | |
| − | Directly force a GPIO to output and set its initial value(high=1 low=0)
| |
| − | # echo high > /sys/class/gpio/gpio27/direction
| |
| − | | |
| − | Used as IRQ signal
| |
| − | | |
| − | Note:You have to configure GPIO to input
| |
| − | # echo "rising" > /sys/class/gpio/gpio27/edge
| |
| − | *rising: Trigger on rising edge
| |
| − | *falling: Trigger on falling edge
| |
| − | *both: Trigger on both edges
| |
| − | *none: Disable interrupt on both edges
| |
| − | | |
| − | Unexport GPIO 27
| |
| − | # echo 27 /sys/class/gpio/unexport
| |
| − | | |
| − | ====Testing====
| |
| − | GPIO 27 and GPIO 29 are taken as an example:
| |
| − | *Connect GPIO 27 and GPIO 29
| |
| − | *Export GPIO 27 and GPIO 29
| |
| − | # echo 27 /sys/class/gpio/export
| |
| − | # echo 29 /sys/class/gpio/export
| |
| − | *Set GPIO 27 to output
| |
| − | # echo "out" > /sys/class/gpio/gpio27/direction
| |
| − | *Set GPIO 29 to input
| |
| − | # echo "in" > /sys/class/gpio/gpio29/direction
| |
| − | *Change GPIO 27 to 1 and read GPIO 29 value
| |
| − | # echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio27/value
| |
| − | # cat /sys/class/gpio/gpio29/value
| |
| − | 1
| |
| − | *Change GPIO 27 to 0 and read GPIO 29 value
| |
| − | # echo 0 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio27/value
| |
| − | # cat /sys/class/gpio/gpio29/value
| |
| − | 0
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==GPS==
| |
| − | ===GPS module ublox 5===
| |
| − | * linux kernel config
| |
| − | <tt><small>
| |
| − | ::Device Drivers --->
| |
| − | :::[*] USB support --->
| |
| − | ::::<*> USB Modem (CDC ACM) support
| |
| − | ::::[*] USB Gadget Support
| |
| − | :::::[m] USB Gadget Drivers
| |
| − | | |
| − | ::[*] USB support --->
| |
| − | :::[*] Support for Freescale on-chip EHCI USB controller
| |
| − | :::<*> USB Serial Converter support --->
| |
| − | ::::[*] USB Generic Serial Driver
| |
| − | </small></tt>
| |
| − | * list usb device
| |
| − | *:no device
| |
| − | *:[[File:GPS_ublox_5_lsusb_nodevice.png|280px]]
| |
| − | *:device plugged in
| |
| − | *:[[File:GPS_ublox_5_lsusb.png|280px]]
| |
| − | * testing
| |
| − | *:[[File:GPS_ublox_5_real_test.png|600px]]
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==I2C==
| |
| − | ===Testing===
| |
| − | Check i2c busses
| |
| − | *Usage: i2cdetect [-y] [-a] [-q|-r] I2CBUS [FIRST LAST]
| |
| − | #i2cdetect -l
| |
| − | i2c-0 i2c 21a0000.i2c I2C adapter
| |
| − | i2c-1 i2c 21a4000.i2c I2C adapter
| |
| − | i2c-2 i2c 21a8000.i2c I2C adapter
| |
| − | | |
| − | Check devices on i2c-2 bus
| |
| − | #i2cdetect -y -r 2
| |
| − | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f
| |
| − | 00: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
| |
| − | 10: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
| |
| − | 20: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
| |
| − | 30: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
| |
| − | 40: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
| |
| − | 50: UU UU -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
| |
| − | 60: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
| |
| − | 70: -- -- -- -- -- -- UU --
| |
| − | | |
| − | Dump I2C device register content
| |
| − | *Usage: i2cdump [-f] [-y] [-r first-last] I2CBUS ADDRESS [MODE [BANK [BANKREG]]]
| |
| − | # i2cdump -y -f 2 0x76
| |
| − | No size specified (using byte-data access)
| |
| − | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f 0123456789abcdef
| |
| − | 00: 54 00 80 43 40 40 40 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ff ff T.?C@@@S........
| |
| − | 10: 85 ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ?...............
| |
| − | 20: 00 00 00 18 ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ...?............
| |
| − | 30: ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ................
| |
| − | 40: ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ................
| |
| − | 50: ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ................
| |
| − | 60: ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ................
| |
| − | 70: ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ................
| |
| − | 80: 54 00 80 43 40 40 40 53 00 00 00 00 00 00 ff ff T.?C@@@S........
| |
| − | 90: 85 ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ?...............
| |
| − | a0: 00 00 00 18 ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ...?............
| |
| − | b0: ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ................
| |
| − | c0: ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ................
| |
| − | d0: ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ................
| |
| − | e0: ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ................
| |
| − | f0: ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ................
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Read a single byte
| |
| − | *Usage: i2cget [-f] [-y] I2CBUS CHIP-ADDRESS [DATA-ADDRESS [MODE]]
| |
| − | # i2cget -f -y 2 0x76 7
| |
| − | 0x00
| |
| − | | |
| − | Change its value and verify it
| |
| − | *Usage: i2cset [-f] [-y] [-m MASK] [-r] I2CBUS CHIP-ADDRESS DATA-ADDRESS [VALUE] ... [MODE]
| |
| − | # i2cset -f -y 2 0x76 7 0x53
| |
| − | # i2cget -f -y 2 0x76 7
| |
| − | 0x53
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==IR==
| |
| − | To decode the infrared signals and provide an uniform interface
| |
| − | lircd -d /dev/lirc0
| |
| − | | |
| − | used parameters:
| |
| − | -d --device=device read from given device
| |
| − | -u --uinput generate Linux input events
| |
| − | | |
| − | Executes commands on an IR signal decoded by lircd,
| |
| − | irexec -d /devlirc0
| |
| − | | |
| − | Note:
| |
| − | if show these message after running lircd
| |
| − | lircd: can't open or create /var/run/lirc/lircd.pid
| |
| − | lircd: No such file or directory
| |
| − | It has to add the "/var/run/lirc" folder
| |
| − | mkdir /var/run/lirc
| |
| − | | |
| − | How to debug:
| |
| | | | |
| − | 1. To check that signals are decoded correctly
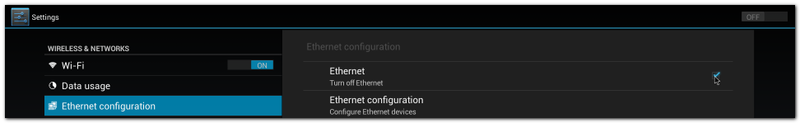
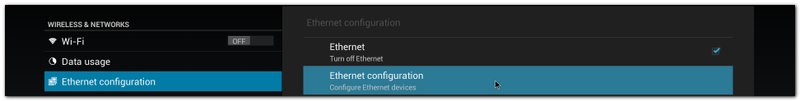
| + | #Click "Settings" / "Ethernet configuration" , then Turn on Ethernet |
| − | mode2 -d /dev/lirc0
| + | #:[[File:Imx6ABV1 settings ethernet config.png|800px|Imx6ABV1 settings ethernet config.png]] |
| − | It repeats to show "space" and "pulse" while clicking a control button
| + | #Click "Ethernet configuration" |
| − | space 8451531
| + | #:[[File:Imx6ABV1 settings ethernet config next level.png|800px|Imx6ABV1 settings ethernet config next level.png]] |
| − | pulse 476
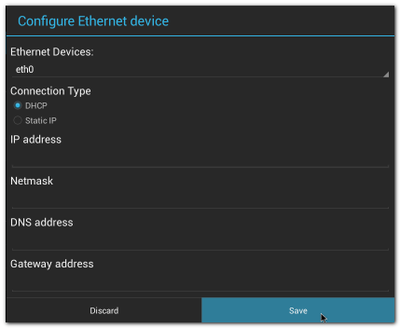
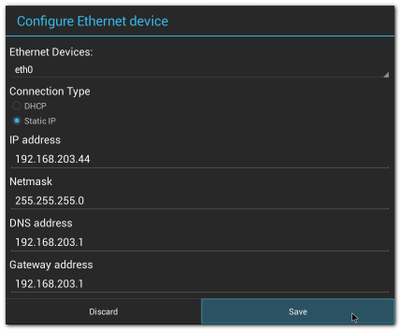
| + | #Choose Connection Type (DHCP or Static IP) |
| | + | #:[[File:Imx6ABV1 settings ethernet config dhcp.png|400px|Imx6ABV1 settings ethernet config dhcp.png]][[File:Imx6ABV1 settings ethernet config static.png|400px|Imx6ABV1 settings ethernet config static.png]] |
| | | | |
| − | 2. To check input events.
| + | == Update System == |
| | | | |
| − | First, It must add the parameter,"-u", in lircd command
| + | #Refer to 1.4.6 to build OTA package. |
| − | lircd -d /dev/lirc0 -u
| + | #Plug SD card that contains OTA package(update.zip) into SD slot. |
| − | It will register at inputX,
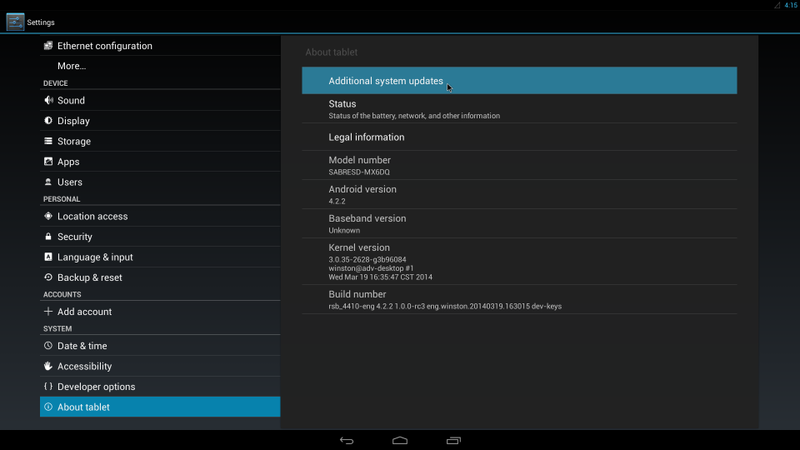
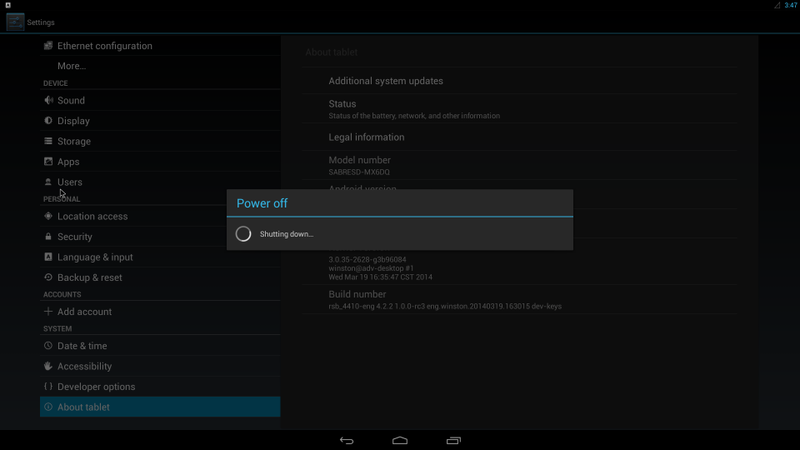
| + | #Click "Settings" / "About tablet" / "Addition system updates" : |
| − | input: lircd as /devices/virtual/input/input1
| + | #:[[File:Imx6ABV1 settings addition system updates.png|800px|Imx6ABV1 settings addition system updates.png]] |
| − | Run evtest to check events
| + | #Wait for one moment, system will reboot for updating |
| − | evtest -d /dev/input/event1
| + | #:[[File:Imx6ABV1 poweroff.png|800px|Imx6ABV1 poweroff.png]] |
| | + | #It will take some time to update. |
| | | | |
| − | ==One Wire== | + | == Watchdog == |
| − | Example
| |
| | | | |
| − | ==RTC==
| |
| | Example | | Example |
| | | | |
| − | ==SATA== | + | == Fastboot == |
| − | ===SATA speed===
| |
| − | Check SATA speed
| |
| − | # dmesg| grep "SATA link up"
| |
| − | [ 1.983660] ata1: SATA link up 3.0 Gbps (SStatus 123 SControl 300)
| |
| | | | |
| − | Change SATA speed
| + | #<span style="font-family:times new roman,times,serif;"><span style="font-size:small;">Fastboot is a feature which can be used to download images from a computer running either Windows OS or Linux OS to the target storage device.</span></span> |
| − | *Add 'libata.force=1.5Gbps' to kernel boot arguments in U-boot
| |
| − | #setenv sataargs $sataargs libata.force=1.5Gbps
| |
| | | | |
| − | Verify
| + | ---- |
| − | # dmesg| grep "SATA link up"
| |
| − | [ 1.993678] ata1: SATA link up 1.5 Gbps (SStatus 113 SControl 310)
| |
| | | | |
| − | ===Testing=== | + | <span style="font-family:times new roman,times,serif;"><span style="font-size:small;">[Target side]</span></span> |
| − | Insert SATA disk before boot
| |
| − | #find /sys/ . -name block | grep ata | xargs ls $1
| |
| − | sda
| |
| | | | |
| − | *According to the above content, we can know sda is our SATA disk
| + | #<span style="font-family:times new roman,times,serif;"><span style="font-size:small;">Power on the board with USB OTG connected</span></span> |
| | + | #<span style="font-family:times new roman,times,serif;"><span style="font-size:small;">Press any key to enter the U-Boot shell</span></span> |
| | + | #<span style="font-family:times new roman,times,serif;"><span style="font-size:small;">Select the correct device to do fastboot image download by command</span></span> |
| | | | |
| − | Generate random file
| + | <span style="font-family:times new roman,times,serif;"><span style="font-size:small;">[Uboot] Run the fastboot command:</span></span> |
| − | # dd if=/dev/urandom of=data bs=1 count=1024
| |
| | | | |
| − | Back up
| + | <small><big><span style="font-family:times new roman,times,serif;"> </span></big></small><small><big> </big></small><span style="font-family:courier new,courier,monospace;"><small>$ fastboot</small></span> |
| − | # dd if=/dev/sda of=backup bs=1 count=1024 skip=4096 | |
| | | | |
| − | Write to SATA disk
| + | <span style="font-family:times new roman,times,serif;"><span style="font-size:small;">[Kernel] you can input this command in the kernel:</span></span> |
| − | # dd if=data of=/dev/sda bs=1 seek=4096
| |
| | | | |
| − | Read and Verify
| + | <small> </small><span style="font-family:courier new,courier,monospace;"><small> $ reboot bootloader ### the board reset to fastboot mode.</small></span> |
| − | # dd if=/dev/sda of=data1 bs=1 count=1024 skip=4096 | |
| − | # diff data data1
| |
| − | If fail, it shows as below:
| |
| − | Binary files data1 and data differ
| |
| | | | |
| − | Restore
| + | ---- |
| − | # dd if=backup of=/dev/sda bs=1 seek=4096
| |
| | | | |
| − | ==SD/MMC== | + | <span style="font-family:times new roman,times,serif;"><span style="font-size:small;">[Host side]</span></span> |
| − | ===Testing===
| |
| − | Check sysfs node
| |
| − | # cat /sys/block/mmcblk0/device/type
| |
| − | MMC
| |
| − | # cat /sys/block/mmcblk1/device/type
| |
| − | SD
| |
| | | | |
| − | SD Card is taken as an example:
| + | #<span style="font-size:small;"><span style="font-family:times new roman,times,serif;">Enter the Android SDK tools directory and find the fastboot utility (fastboot.exe on the Windows OS, fastboot on the Linux OS)</span></span> |
| − | Generate random file
| + | #<span style="font-size:small;"><span style="font-family:times new roman,times,serif;">Copy all downloaded images to the "images" folder</span></span> |
| − | # dd if=/dev/urandom of=data bs=1 count=1024
| + | #<span style="font-size:small;"><span style="font-family:times new roman,times,serif;">Run the following commands to flash the SD or eMMC</span></span> |
| | | | |
| − | Back up
| + | <span style="font-family:times new roman,times,serif;"><small> </small></span><span style="font-family:courier new,courier,monospace;"><small>$ fastboot flash boot images\boot.img</small></span> |
| − | # dd if=/dev/mmcblk1 of=backup bs=1 count=1024 skip=4096 | |
| | | | |
| − | Write to SD
| + | <span style="font-family:times new roman,times,serif;"><small> </small></span><span style="font-family:courier new,courier,monospace;"><small> $ fastboot flash system images\system.img</small></span> |
| − | # dd if=data of=/dev/mmcblk1 bs=1 seek=4096 | |
| | | | |
| − | Read and Verify
| + | <span style="font-family:times new roman,times,serif;"><small> </small></span><span style="font-family:courier new,courier,monospace;"><small>$ fastboot flash recovery images\recovery.img</small></span> |
| − | # dd if=/dev/mmcblk1 of=data1 bs=1 count=1024 skip=4096 | |
| − | # diff data data1
| |
| − | If fail, it shows as below:
| |
| − | Binary files data1 and data differ
| |
| | | | |
| − | Restore
| + | <span style="font-family:times new roman,times,serif;"><small> </small></span><span style="font-family:courier new,courier,monospace;"><small> $ fastboot reboot</small></span> |
| − | # dd if=backup of=/dev/mmcblk1 bs=1 seek=4096 | |
| − | | |
| − | ==SPI==
| |
| − | Example
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==SPWG/JEDIA==
| |
| − | Standard Panels Working Group '''(SPWG)'''
| |
| − | | |
| − | Japan Electronic Industry Development Association '''(JEIDA)'''
| |
| − | | |
| − | How to setting '''SPWG/JEIDA''' mode in RISC?
| |
| − | | |
| − | Modify Register '''GPR(IOMUXC_GPR2)'''value
| |
| − | | |
| − | Address : 0x020E0008(h)
| |
| − | | |
| − | BIT6 and BIT8 set "0" '''(SPWG)'''
| |
| − | | |
| − | BIT6 and BIT8 set "1" '''(JEIDA)'''
| |
| − |
| |
| − | :[[Image:JEIDA1.png|350px]] | |
| − | :[[Image:JEIDA2.png|350px]]
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==UART==
| |
| − | ===RS-232===
| |
| − | ====Configuration ====
| |
| − | Connect UART1(ttymxc1) TX and RX
| |
| − | | |
| − | Use stty command to set baudrate
| |
| − | # stty -F /dev/ttymxc1 115200
| |
| − | | |
| − | ====Testing====
| |
| − | Check baudrate
| |
| − | # stty -F /dev/ttymxc1 115200
| |
| − | speed 115200 baud; line = 0;
| |
| − | | |
| − | Read
| |
| − | #cat /dev/ttymxc1 &
| |
| − | | |
| − | Send
| |
| − | #echo test > /dev/ttymxc1
| |
| − | test
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==USB== | |
| − | ===Host===
| |
| − | ====Testing====
| |
| − | Insert a USB disk
| |
| − | usb 1-1.2: new high-speed USB device number 4 using ci_hdrc
| |
| − | usb-storage 1-1.2:1.0: USB Mass Storage device detected
| |
| − | scsi2 : usb-storage 1-1.2:1.0
| |
| − | scsi 2:0:0:0: Direct-Access Generic- SD/MMC 1.00 PQ: 0 ANSI: 0 CCS
| |
| − | sd 2:0:0:0: [sda] 3862528 512-byte logical blocks: (1.97 GB/1.84 GiB)
| |
| − | sd 2:0:0:0: [sda] Write Protect is off
| |
| − | sd 2:0:0:0: [sda] No Caching mode page found
| |
| − | sd 2:0:0:0: [sda] Assuming drive cache: write through
| |
| − | sd 2:0:0:0: [sda] No Caching mode page found
| |
| − | sd 2:0:0:0: [sda] Assuming drive cache: write through
| |
| − | sda: sda1
| |
| − | sd 2:0:0:0: [sda] No Caching mode page found
| |
| − | sd 2:0:0:0: [sda] Assuming drive cache: write through
| |
| − | sd 2:0:0:0: [sda] Attached SCSI removable disk
| |
| − | | |
| − | *According to the above content, we can know sda is our usb disk
| |
| − | | |
| − | Generate random file
| |
| − | # dd if=/dev/urandom of=data bs=1 count=1024
| |
| − | | |
| − | Back up
| |
| − | # dd if=/dev/sda of=backup bs=1 count=1024 skip=4096
| |
| − | | |
| − | Write to usb disk
| |
| − | # dd if=data of=/dev/sda bs=1 seek=4096
| |
| − | | |
| − | Read and Verify
| |
| − | # dd if=/dev/sda of=data1 bs=1 count=1024 skip=4096
| |
| − | # diff data data1
| |
| − | If fail, it shows as below:
| |
| − | Binary files data1 and data differ | |
| − | | |
| − | Restore
| |
| − | # dd if=backup of=/dev/sda bs=1 seek=4096
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Client===
| |
| − | ====Testing====
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==Watchdog==
| |
| − | Example
| |