Difference between revisions of "WISE-1530 RF Continue Tx Manual"
Erick.huang (talk | contribs) |
Erick.huang (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
<span style="background-color:#D3D3D3;">Ex: join join RT66 wpa2_aes 987135238</span> | <span style="background-color:#D3D3D3;">Ex: join join RT66 wpa2_aes 987135238</span> | ||
| − | + | '''Ping: ''' | |
ping <destination> [-i <interval in ms>] [-n <number>] [-l <length>] | ping <destination> [-i <interval in ms>] [-n <number>] [-l <length>] | ||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
-t: time(second) | -t: time(second) | ||
| − | <span style="background-color:#D3D3D3;">Ex | + | <span style="background-color:#D3D3D3;">Ex: iperf -c 192.168.1.1 -u -t 30</span> |
[[Category:Editor]] | [[Category:Editor]] | ||
Revision as of 03:39, 19 July 2017
Preparing for Hardware
The user needs to prepare for hardware as following:
- WISE-1530, WISE-1500 and WISE-ED22.
- 802.11b/g/n (2.4 GHz) Wireless Access Point (AP).
- PC running the Microsoft® Windows® 7 operating systems
Please refer to the following steps for setup a WISE-1530 boards.
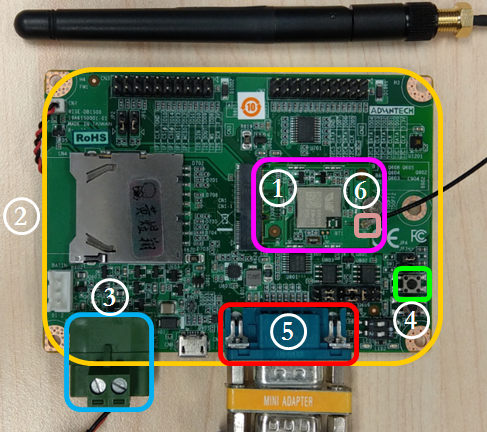
Step01: Please prepare boards as below.
① WISE-1530
② WISE-1500
③ Power connector
④ Reset button
⑤ UART connector
⑥ RF connector
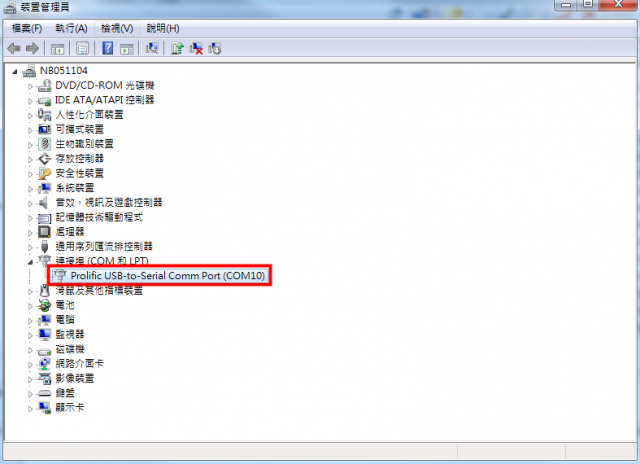
Step02: Connect the WISE-1530 to PC via USB-to-UART cable.
- Install USB-to-UART driver.
- The device will be visible in the Device Manager as below, user can use serial port tools (putty, tera term ...etc.).
RF Test Command
You can see " Console app start, type 'help' " on console screen, after power on.
Join: Connect to AP
join <ssid> <open|wpa_aes|wpa_tkip|wpa2|wpa2_tkip|wpa2_aes|wep> [key] [channel] [ip netmask gateway]
Ex: join join RT66 wpa2_aes 987135238
Ping:
ping <destination> [-i <interval in ms>] [-n <number>] [-l <length>]
Ex: ping 192.168.1.1 -i 10 -n 10
Iperf: Test Tx
iperf [-s|-c host ip] [options]
-u: use UDP mode
-t: time(second)
Ex: iperf -c 192.168.1.1 -u -t 30