Difference between revisions of "AOM-DB3500 UART(DEBUG、COM1、M.2 E-Key)"
Xingxing.li (talk | contribs) |
Xingxing.li (talk | contribs) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
| style="width: 169px;" | NC | | style="width: 169px;" | NC | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=== '''Debug Port Settings''' === | === '''Debug Port Settings''' === | ||
| Line 69: | Line 67: | ||
=== '''COM1_2——COM1''' === | === '''COM1_2——COM1''' === | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:AOM-DB3500 COM1 2.png|600x500px|AOM-DB3500 COM1 2.png]] [[File:AOM-DB3500 COM1 2 Pin header.png|RTENOTITLE]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| border="1" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" style="width: 500px;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="4" | '''COM1_2 Connector,COM1 RS232 Mode Pin Definition''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Pin''' | ||
| + | | '''Signal''' | ||
| + | | '''I/O''' | ||
| + | | '''Description''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1 | ||
| + | | N/A | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Not Applicable | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2 | ||
| + | | N/A | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Not Applicable | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 3 | ||
| + | | COM1_RX_485+ | ||
| + | | O | ||
| + | | COM1 RS232 Receive Data | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 4 | ||
| + | | COM1_RTS# | ||
| + | | I | ||
| + | | COM1 Request to Send | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 5 | ||
| + | | COM1_TXD_422- | ||
| + | | I | ||
| + | | COM1 RS232 Transmit Data | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 6 | ||
| + | | COM1_CTS# | ||
| + | | O | ||
| + | | COM1 Clear to Send | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 7 | ||
| + | | N/A | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Not Applicable | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 8 | ||
| + | | N/A | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Not Applicable | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 9 | ||
| + | | GND | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Ground | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 10 | ||
| + | | GND | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Ground | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 11 | ||
| + | | N/A | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Not Applicable | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 12 | ||
| + | | N/A | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Not Applicable | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 13 | ||
| + | | COM2_RX_485+ | ||
| + | | O | ||
| + | | COM2 RS232 Receive Data | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 14 | ||
| + | | COM2_RTS# | ||
| + | | I | ||
| + | | COM2 Request to Send | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 15 | ||
| + | | COM2_TXD_422- | ||
| + | | I | ||
| + | | COM2 RS232 Transmit Data | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 16 | ||
| + | | COM2_CTS# | ||
| + | | O | ||
| + | | COM2 Clear to Send | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 17 | ||
| + | | N/A | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Not Applicable | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 18 | ||
| + | | N/A | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Not Applicable | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 19 | ||
| + | | GND | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Ground | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 20 | ||
| + | | GND | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Ground | ||
| + | |} | ||
| | ||
| − | === ''' | + | === '''Configure Parameters''' === |
| − | | + | Use “stty” command to configure serial port parameters. The commonly used parameters include “Baud rate”, “Data bits”, “Stop bits”, “Parity”, “Flow control”. |
| + | |||
| + | See details of the usage of “stty”: | ||
| + | <pre># stty --help | ||
| + | … … | ||
| + | csN set character size to N bits, N in [5..8] | ||
| + | [-]cstopb use two stop bits per character (one with '-') | ||
| + | [-]parenb generate parity bit in output and expect parity bit in input | ||
| + | [-]crtscts enable RTS/CTS handshaking | ||
| + | …</pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | For example, set COM1<br/> “Baud rate” to 115200<br/> “Data bits” to 8<br/> “Stop bits” to 1<br/> “Parity” to None<br/> “Flow control” to None | ||
| + | <pre># stty -F /dev/ttyS0 115200 cs8 -parenb -cstopb</pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === '''Send and receive data''' === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Taking COM1 as receiver or sender (An external COM is required to do the sendingor receiving). For example, AOM-3821 is responsible for receiving and inputting instructions. The PC computer is connected via a cable and COM1. The PC computer uses the PuTTY serial port tool, opens the COM port, configures the baud rate to 115200, data bits to 8, stop bits to 1, parity to none, flow control to none, and sends "pass" to the serial port assistant. If no error, the external COM receiver will receive “pass”. | ||
| + | <pre># #---- COM1 as receiver ----# # | ||
| + | # stty -F /dev/ttyS0 115200 cs8 -cstopb -parenb | ||
| + | # cat /dev/ttyS0 &</pre> | ||
| + | <pre># #---- COM1 as sender ----# # | ||
| + | # stty -F /dev/ttyS0 115200 cs8 -cstopb -parenb | ||
| + | # echo pass > /dev/ttyS0 | ||
| + | # #----If no error, the external COM receiver will receive “pass”----# # | ||
| + | pass</pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note! | ||
| − | | + | 1.Receiver should run before sender.<br/> 2.The "serial port parameters" should be the same for sender and receiver. |
Latest revision as of 09:22, 30 December 2025
Contents
UART
User Debian/Linux UART/serial port access is through the tty-devices. The ttydevices have different names depending on UART drivers for different boards.
| Device Node | COM Port Name |
| /dev/ttyFIQ0 | Debug |
| /dev/ttyS0 | COM1(COM1_2 connnector RS232 2-wire) |
| /dev/ttyS6 | M.2_E1(UART) |
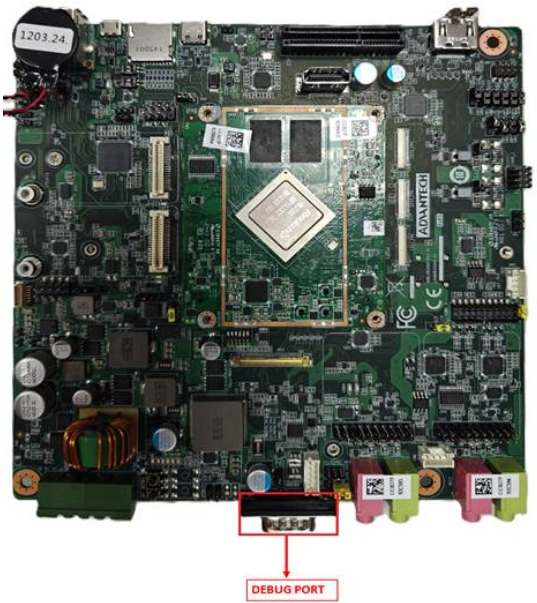
DEBUG Port Connection
1.Connect the debug port cable on AOM-DB3500.
2.Connect it to your PC with a USB to COM Cable.
| DEBUG Pin Connector | |
| Pin | Signal |
| 1 | NC |
| 2 | RX_DEBUG |
| 3 | TX_DEBUG |
| 4 | NC |
| 5 | GND |
| 6 | NC |
| 7 | RTS# |
| 8 | CTS# |
| 9 | NC |
Debug Port Settings
AOM-3821 can communicate with a host server using serial cables. Common serial communication programs such as HyperTerminal, Tera Term, or PuTTY can be used in this case. The example below describes the serial terminal setup using HyperTerminal on a Windows host:
1. Connect AOM-3821 with your PC using a serial cable.
2. Open HyperTerminal on your Windows PC, and select the settings demonstrated in the photo below.
3. Insert a power adapter into the DC jack and power up the board. The Debug console log will be displayed on the terminal screen.
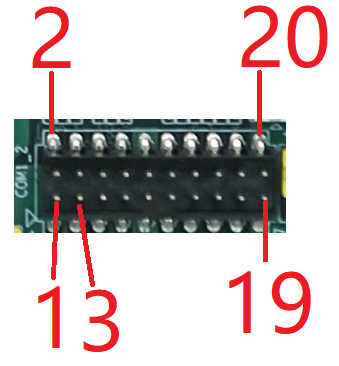
COM1_2——COM1
| COM1_2 Connector,COM1 RS232 Mode Pin Definition | |||
| Pin | Signal | I/O | Description |
| 1 | N/A | Not Applicable | |
| 2 | N/A | Not Applicable | |
| 3 | COM1_RX_485+ | O | COM1 RS232 Receive Data |
| 4 | COM1_RTS# | I | COM1 Request to Send |
| 5 | COM1_TXD_422- | I | COM1 RS232 Transmit Data |
| 6 | COM1_CTS# | O | COM1 Clear to Send |
| 7 | N/A | Not Applicable | |
| 8 | N/A | Not Applicable | |
| 9 | GND | Ground | |
| 10 | GND | Ground | |
| 11 | N/A | Not Applicable | |
| 12 | N/A | Not Applicable | |
| 13 | COM2_RX_485+ | O | COM2 RS232 Receive Data |
| 14 | COM2_RTS# | I | COM2 Request to Send |
| 15 | COM2_TXD_422- | I | COM2 RS232 Transmit Data |
| 16 | COM2_CTS# | O | COM2 Clear to Send |
| 17 | N/A | Not Applicable | |
| 18 | N/A | Not Applicable | |
| 19 | GND | Ground | |
| 20 | GND | Ground | |
Configure Parameters
Use “stty” command to configure serial port parameters. The commonly used parameters include “Baud rate”, “Data bits”, “Stop bits”, “Parity”, “Flow control”.
See details of the usage of “stty”:
# stty --help … … csN set character size to N bits, N in [5..8] [-]cstopb use two stop bits per character (one with '-') [-]parenb generate parity bit in output and expect parity bit in input [-]crtscts enable RTS/CTS handshaking …
For example, set COM1
“Baud rate” to 115200
“Data bits” to 8
“Stop bits” to 1
“Parity” to None
“Flow control” to None
# stty -F /dev/ttyS0 115200 cs8 -parenb -cstopb
Send and receive data
Taking COM1 as receiver or sender (An external COM is required to do the sendingor receiving). For example, AOM-3821 is responsible for receiving and inputting instructions. The PC computer is connected via a cable and COM1. The PC computer uses the PuTTY serial port tool, opens the COM port, configures the baud rate to 115200, data bits to 8, stop bits to 1, parity to none, flow control to none, and sends "pass" to the serial port assistant. If no error, the external COM receiver will receive “pass”.
# #---- COM1 as receiver ----# # # stty -F /dev/ttyS0 115200 cs8 -cstopb -parenb # cat /dev/ttyS0 &
# #---- COM1 as sender ----# # # stty -F /dev/ttyS0 115200 cs8 -cstopb -parenb # echo pass > /dev/ttyS0 # #----If no error, the external COM receiver will receive “pass”----# # pass
Note!
1.Receiver should run before sender.
2.The "serial port parameters" should be the same for sender and receiver.