Difference between revisions of "AFE-R761 CAN/DEBUG"
Xingxing.li (talk | contribs) (Created page with " === '''Hardware Pin Definition:''' === {| border="1" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" style="width: 299px;" |- | colspan="2" style="width: 289px;" | '''CAN/DEBUG Connector'...") |
Xingxing.li (talk | contribs) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
| style="width: 200px;" | CAN1_L | | style="width: 200px;" | CAN1_L | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | === [[File:AFE-R761 CAN Number.jpg]] === | ||
=== '''Debug Port Connection:''' === | === '''Debug Port Connection:''' === | ||
| − | 1. Connect the debug port cable (1700035538-01) to the Debug port on | + | 1. Connect the debug port cable (1700035538-01) to the Debug port on AFE-R761. |
2. Connect it to your PC using the USB to RS-232 Cable. | 2. Connect it to your PC using the USB to RS-232 Cable. | ||
| Line 42: | Line 44: | ||
=== '''Debug Port Settings:''' === | === '''Debug Port Settings:''' === | ||
| − | AFE-R761 can communicate with a host server using serial cables. Common serial communication programs such as HyperTerminal, Tera Term, or PuTTY can be used in these applications. The example below describes the serial terminal setup using<br/> HyperTerminal on a Windows host:<br/> 1. Connect AFE-R761 with your PC using a serial cable. | + | AFE-R761 can communicate with a host server using serial cables. Common serial communication programs such as HyperTerminal, Tera Term, or PuTTY can be used in these applications. The example below describes the serial terminal setup using<br/> HyperTerminal on a Windows host:<br/> 1. Connect AFE-R761 with your PC using a serial cable. |
| − | |||
| + | 2. Open HyperTerminal on your Windows PC, and select the settings demonstrated in the photo below. | ||
3. Insert power adapter to DC jack and power up the board. The Debug console log will be displayed on the terminal screen. | 3. Insert power adapter to DC jack and power up the board. The Debug console log will be displayed on the terminal screen. | ||
| Line 74: | Line 76: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | === '''Configure''' === | + | ==== '''Configure''' ==== |
Use “ip” command to configure can port. See details of the usage of “ip link”: | Use “ip” command to configure can port. See details of the usage of “ip link”: | ||
| Line 125: | Line 127: | ||
# cansend --help</pre> | # cansend --help</pre> | ||
| − | [[File:AFE-R761 CAN RM01.png]] | + | [[File:AFE-R761 CAN RM01.png|RTENOTITLE]] |
| − | [[File:AFE-R761 CAN RM02.png]] | + | [[File:AFE-R761 CAN RM02.png|RTENOTITLE]] |
Latest revision as of 02:56, 13 January 2026
Contents
Hardware Pin Definition:
| CAN/DEBUG Connector | |
| Pin | Pin Name |
| 1 | TX_DEBUG |
| 2 | RX_DEBUG |
| 3 | GND |
| 4 | GND |
| 5 | CAN2_H |
| 6 | CAN2_L |
| 7 | CAN1_H |
| 8 | CAN1_L |
Debug Port Connection:
1. Connect the debug port cable (1700035538-01) to the Debug port on AFE-R761.
2. Connect it to your PC using the USB to RS-232 Cable.
Debug Port Settings:
AFE-R761 can communicate with a host server using serial cables. Common serial communication programs such as HyperTerminal, Tera Term, or PuTTY can be used in these applications. The example below describes the serial terminal setup using
HyperTerminal on a Windows host:
1. Connect AFE-R761 with your PC using a serial cable.
2. Open HyperTerminal on your Windows PC, and select the settings demonstrated in the photo below.
3. Insert power adapter to DC jack and power up the board. The Debug console log will be displayed on the terminal screen.
CAN
AFE-R761 has two CAN ports.
Use the "candump" and "cansend" tools directly to send and receive messages. The tools have been embedded into the system.
Check network ports
Check network ports of can0 and can1:
# ifconfig -a … … can0: flags=193<UP,RUNNING,NOARP> mtu 16 unspec 00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00 txqueuelen 10 (UNSPEC) RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B) RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0 can1: flags=193<UP,RUNNING,NOARP> mtu 16 unspec 00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00 txqueuelen 10 (UNSPEC) RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B) RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0 … …
Configure
Use “ip” command to configure can port. See details of the usage of “ip link”:
# ip link help
… …
ip link set { DEVICE | dev DEVICE | group DEVGROUP }
[ { up | down } ]
[ type TYPE ARGS ]
… …
# ip link help can
… …
ip link set DEVICE type can
[ bitrate BITRATE [ sample-point SAMPLE-POINT] ] |
[ dbitrate BITRATE [ dsample-point SAMPLE-POINT] ] |
[ fd { on | off } ]
… …
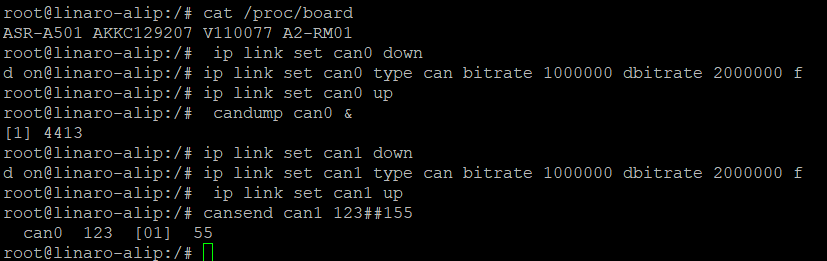
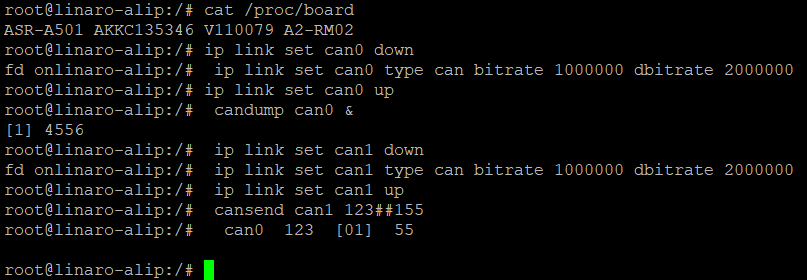
For example, set can0 "birate rate” to 1000000 “dbitrate rate” to 2000000 “fd” to on
# #---- For can0 ----# # # ip link set can0 down # ip link set can0 type can bitrate 1000000 dbitrate 2000000 fd on # ip link set can0 up
Send and Reveive Data
- As receiver
# #---- As receiver ----# # # ip link set can0 down # ip link set can0 type can bitrate 1000000 dbitrate 2000000 fd on # ip link set can0 up # candump can0 &
- As sender
# #---- As sender ----# # # ip link set can1 down # ip link set can1 type can bitrate 1000000 dbitrate 2000000 fd on # ip link set can1 up # cansend can1 123##155 # #----If no error, the receiver will receive the following data----# # Can0 123 [01] 55
See more details of the usage of “candump” and “cansend” :
# candump --help # cansend --help