Difference between revisions of "IoTGateway/BSP/Android/Gettingstarted/How to use UART for rk"
From ESS-WIKI
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== <span style="font-size: medium"><font color="#0066cc">RS-485</font></span> == | == <span style="font-size: medium"><font color="#0066cc">RS-485</font></span> == | ||
| − | RS-485 uses half-duplex communication, which means that one medium is shared for transmitting and receiving data. Therefore the system needs to control the RS-485 transceiver's transmit mode. Usually the UART RTS signal is used to switch the transmitter on and off. | + | RS-485 uses half-duplex communication, which means that one medium is shared for transmitting and receiving data. Therefore the system needs to control the RS-485 transceiver's transmit mode. Usually the UART RTS signal is used to switch the transmitter on and off. |
= '''<span style="font-size: large"><span style="color: rgb(0, 0, 205)">Boards</span></span>''' = | = '''<span style="font-size: large"><span style="color: rgb(0, 0, 205)">Boards</span></span>''' = | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="col" | '''COM Name''' | ! scope="col" | '''COM Name''' | ||
| − | ! scope="col" | '''Device'''<br/> | + | ! scope="col" | '''Device Node'''<br/> |
! scope="col" | | ! scope="col" | | ||
| − | ''' | + | '''Remark''' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | COM1<br/> | + | | style="text-align: center" | UART0<br/> |
| − | | /dev/ | + | | style="text-align: center" | /dev/ttyS0<br/> |
| + | | for BT Data<br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="text-align: center" | COM1<br/> | ||
| + | | style="text-align: center" | /dev/ttyS1<br/> | ||
| <br/> | | <br/> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | COM2<br/> | + | | style="text-align: center" | COM2<br/> |
| − | | /dev/ | + | | style="text-align: center" | /dev/ttyS2<br/> |
| − | | | + | | Debug Port<br/> |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | COM3<br/> | + | | style="text-align: center" | COM3<br/> |
| − | | <br/> | + | | style="text-align: center" | /dev/ttyS3<br/> |
| <br/> | | <br/> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | COM4<br/> | + | | style="text-align: center" | COM4<br/> |
| − | | <br/> | + | | style="text-align: center" | /dev/ttyS4<br/> |
| − | | <br/> | + | | Supprot RSB485<br/> |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | COM5<br/> | + | | style="text-align: center" | COM5<br/> |
| − | | <br/> | + | | style="text-align: center" | /dev/ttyUSB0<br/> |
| − | | <br/> | + | | Usb to Uart<br/> |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | COM6<br/> | + | | style="text-align: center" | COM6<br/> |
| − | | <br/> | + | | style="text-align: center" | /dev/ttyUSB1<br/> |
| − | | <br/> | + | | Usb to Uart<br/> |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 56: | Line 60: | ||
| − | [[File: | + | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
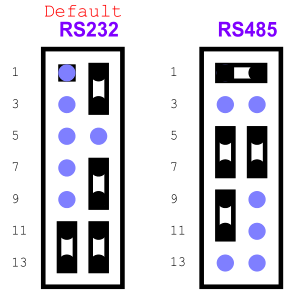
| + | [[File:RS232andRS485Jumper.PNG]] | ||
Revision as of 03:21, 11 April 2018
Contents
Overview
The Android/Linux UART/serial port access from user is through the tty-devices. The tty-devices have different names depending on UART driver on different board.
RS-485
RS-485 uses half-duplex communication, which means that one medium is shared for transmitting and receiving data. Therefore the system needs to control the RS-485 transceiver's transmit mode. Usually the UART RTS signal is used to switch the transmitter on and off.
Boards
RSB4680 Borad
| COM Name | Device Node |
Remark |
|---|---|---|
| UART0 |
/dev/ttyS0 |
for BT Data |
| COM1 |
/dev/ttyS1 |
|
| COM2 |
/dev/ttyS2 |
Debug Port |
| COM3 |
/dev/ttyS3 |
|
| COM4 |
/dev/ttyS4 |
Supprot RSB485 |
| COM5 |
/dev/ttyUSB0 |
Usb to Uart |
| COM6 |
/dev/ttyUSB1 |
Usb to Uart |