Advantech Robotic Suite/DeviceOn
Contents
DeviceOn
A surge in market demand for Industrial IoT products has rapidly increased the number of connected devices that are currently deployed and managed across different locations. It is essential to effectively manage, monitor, and control thousands of connected devices while ensuring uninterrupted service. Devices must work properly and securely after they have been deployed - without requiring frequent visits from service technicians. Customers require secure access to their devices in order to detect, troubleshoot, and undertake time-critical actions.
More information please refer to DeviceOn
How To
Setup WISE-Agent
For EPC-R3720, execute below command to install prerequisites before install WISE-Agent.
apt-get -y install libmosquittopp1 libmosquitto-dev
Then, follow Edge Installation & Onboarding documentation to install WISE-Agent and setup WISE-Agent for connecting to DeviceOn.
Remote Management
Device Management
After your device onboarding, you could view, edit device basic information, remote control, and retrieve sensor data on your devices. Nine sub items under Device, Device List contain device name, upgrade status, power management and etc. Device Monitoring to give device loading at present. To remote diagnostic and debug through Remote Control. Next, all of plugin sensor data from Device Data. To grouping your device through the Device Group. For batch real-time or schedule control through Task defined. Rule Engine to set a threshold rule for your devices data in real-time.
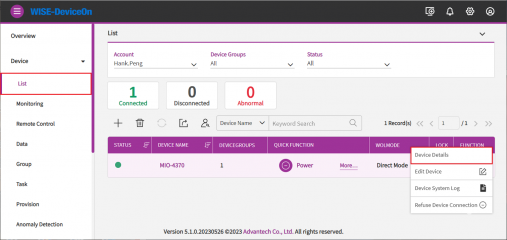
Device List
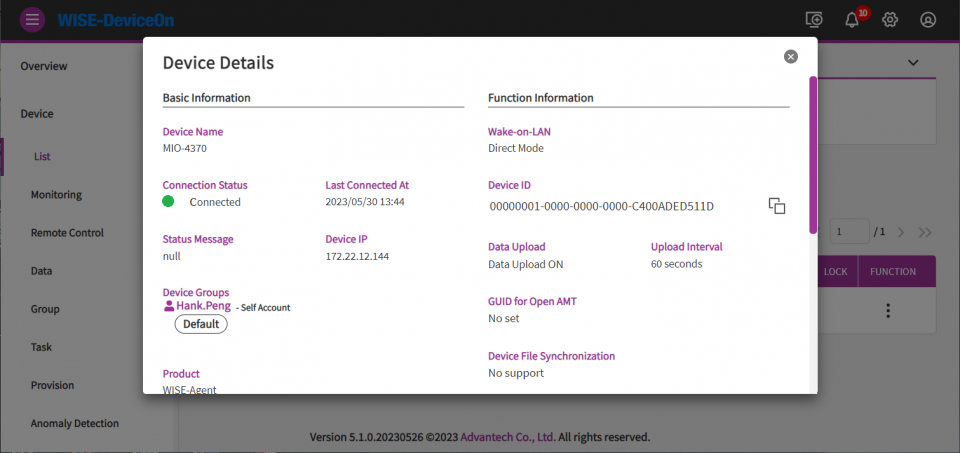
Click on device name or device details to get device information.
You could get the general information such as, device IP, version, MAC, Memory, BIOS, operation system and so on.
Container Management
You can easily set up, deploy, monitor, and manage each container on different devices. For device managers, it can create, manage and set the health of containers within minutes, and provide a variety of container restart strategies. Through the dashboard, you can quickly understand the running status of the container in the managed device. In addition, for container developers, the Azure Container Repository is supported as a public cloud solution, and private cloud uses Harbor as a container repository.
Detailed documentation about Container Management, please refer to DeviceOn Manual - Container Management Section .
Deploy a new ROS 2 Node Container to edge
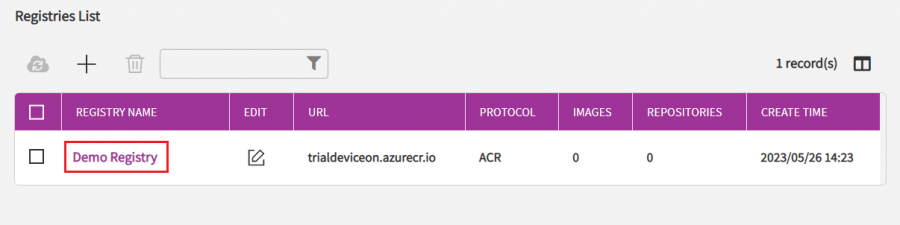
Container of helloworld ROS Node is available in the Azure Container Registry which is named "Demo Registry" in the DeviceOn Portal.
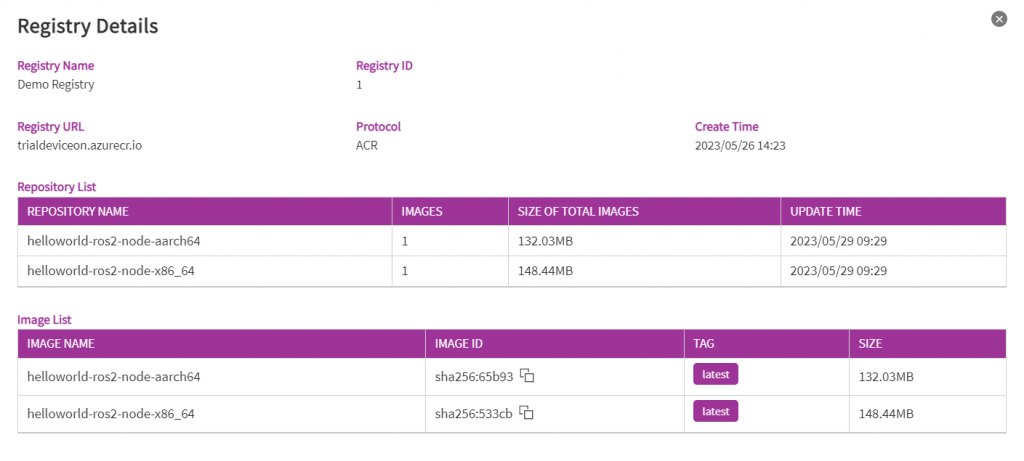
Click on the registry name "Demo Registry", you can see how many containers in the container registry are available for you to deploy.
Follow below steps to start deploy container:
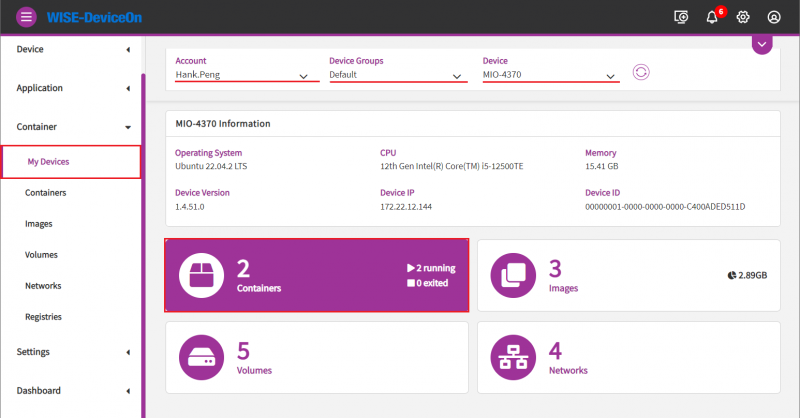
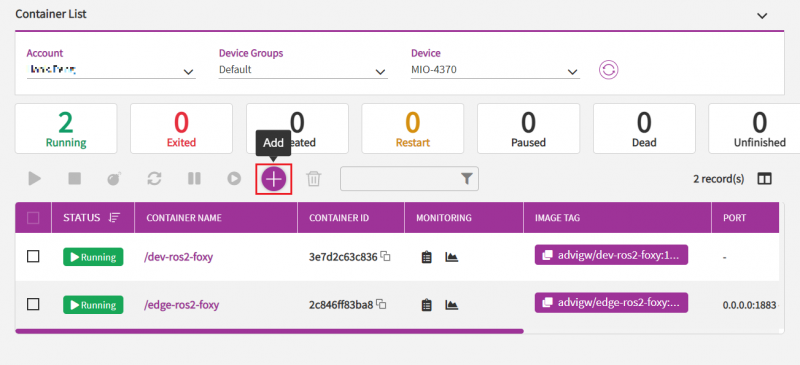
Step1. Go to Container -> My Devices page , choose device for deploy helloworld ros node . Then click Containers icon.
Step2. Click on "Add" icon.
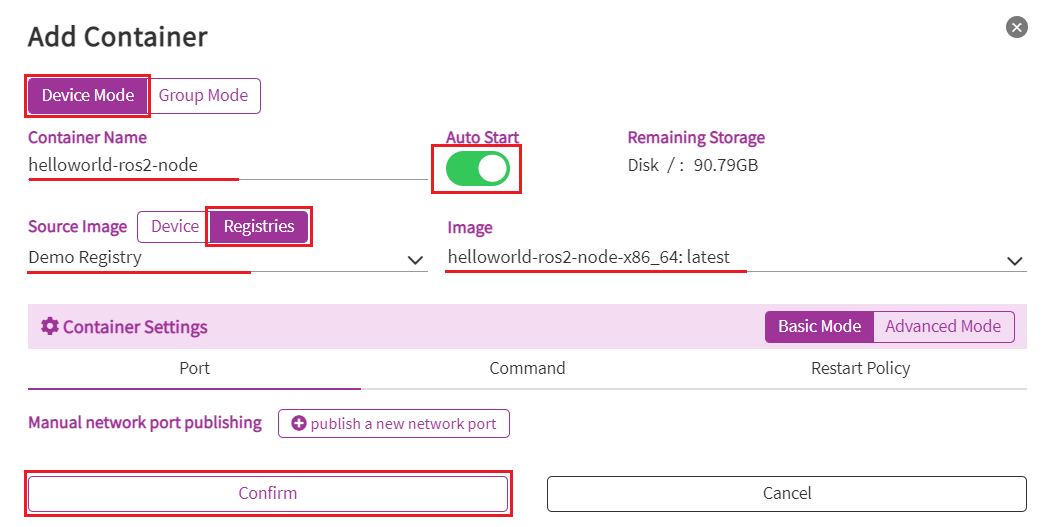
Step3. Select parameters as below:
- Mode: Device Mode
- Container Name: Give a container name by yourdelf.
- Auto Start: On
- Source Image: Registries
- Image: helloworld-ros2-node-<platform-architecture>
If your platform is x86, choose helloworld-ros2-node-x86_64. If your platform is arm, choose helloworld-ros2-node-aarch64.
Click Confirm to start deploy helloworld-ros2-node to the device you choose.
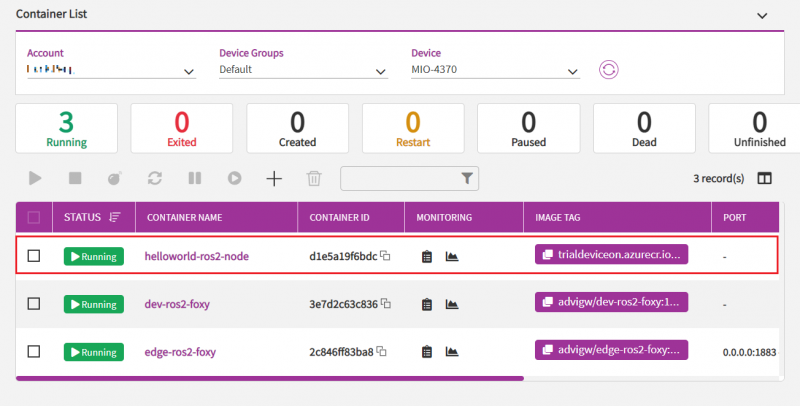
After several seconds, you can see the container is deployed into your device and status of helloworld-ros2-node is running.
Step5. Now, helloworld-ros2-node is running and publishing "Hello World: <count>" message continuously, To subscribe the data that helloworld-ros2-node published, open a terminal from your device and execute below command:
1. Setup ROS2 environmant variables:
$ source /opt/ros/${ROS_DISTRO}/setup.bash
2. Subscribe the topic of helloworld node:
$ ros2 topic echo /topic
Result:
data: 'Hello World: 2663' --- data: 'Hello World: 2664' --- data: 'Hello World: 2665' --- data: 'Hello World: 2666' --- data: 'Hello World: 2667' --- data: 'Hello World: 2668' --- data: 'Hello World: 2669' ---