Difference between revisions of "MCU/WISE-1570 SDK"
(Modify some description for this chapter.) |
|||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
The device will be visible in the Device Manager as below after FTDI driver installed. The user can find the FTDI driver in source tree. | The device will be visible in the Device Manager as below after FTDI driver installed. The user can find the FTDI driver in source tree. | ||
</div><br/> | </div><br/> | ||
| − | |||
== ARM mbed == | == ARM mbed == | ||
<div style="margin-left:0.847cm;margin-right:0cm;"> | <div style="margin-left:0.847cm;margin-right:0cm;"> | ||
| Line 93: | Line 92: | ||
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:git-core/ppa | $ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:git-core/ppa | ||
$ sudo apt-get update | $ sudo apt-get update | ||
| − | $ sudo apt install git | + | $ sudo apt-get install git |
Check the git version | Check the git version | ||
| Line 154: | Line 153: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | |||
=== mbed CLI configuration === | === mbed CLI configuration === | ||
<div style="margin-left:0.847cm;margin-right:0cm;"> | <div style="margin-left:0.847cm;margin-right:0cm;"> | ||
| Line 174: | Line 172: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | |||
= Software API = | = Software API = | ||
| Line 202: | Line 199: | ||
:'''Step01:''' Get source code and compile it by mbed CLI.<br/> | :'''Step01:''' Get source code and compile it by mbed CLI.<br/> | ||
:Please click [https://github.com/ADVANTECH-Corp/WISE-1570-Rf-Bridge "Link to source"] and review the file "README.md" to know how to deployment and compilation with this example. The output binary will be "source_dir/BUILD/WISE_1570/GCC_ARM/WISE-1570-Rf-Bridge.bin"<br/> | :Please click [https://github.com/ADVANTECH-Corp/WISE-1570-Rf-Bridge "Link to source"] and review the file "README.md" to know how to deployment and compilation with this example. The output binary will be "source_dir/BUILD/WISE_1570/GCC_ARM/WISE-1570-Rf-Bridge.bin"<br/> | ||
| + | |||
[[File:WISE-1570-FirstExample 01.png|center|500px|WISE-1570-FirstExample 01.png]] | [[File:WISE-1570-FirstExample 01.png|center|500px|WISE-1570-FirstExample 01.png]] | ||
| − | |||
:'''Step02:''' Flash programming by WISE-ED22<br/> | :'''Step02:''' Flash programming by WISE-ED22<br/> | ||
:Check device connected from WISE-ED22 to PC using micro-USB cable and use drag-and-drop programming with your binary.<br/> | :Check device connected from WISE-ED22 to PC using micro-USB cable and use drag-and-drop programming with your binary.<br/> | ||
| + | |||
[[File:WISE-1570-FirstExample 02.png|center|700px|WISE-1570-FirstExample 02.png]] | [[File:WISE-1570-FirstExample 02.png|center|700px|WISE-1570-FirstExample 02.png]] | ||
| − | |||
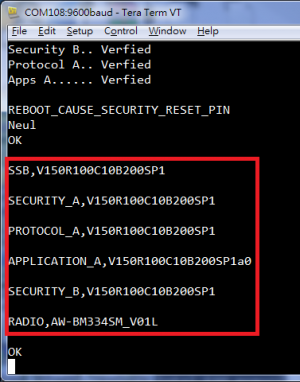
| − | :'''Step03:''' Get the version of RF by AT command "AT+CGMR" | + | :'''Step03:''' Get the version of RF by AT command "AT+CGMR" |
| − | :* Choose any terminal you like. (e.g., the snapshot is setting of Tera Term.) | + | :*Choose any terminal you like. (e.g., the snapshot is setting of Tera Term.) |
| − | :* Please set terminal as the below setting: | + | :*Please set terminal as the below setting: |
::Baud rate: 9600 | ::Baud rate: 9600 | ||
::Data: 8bit | ::Data: 8bit | ||
| Line 218: | Line 215: | ||
::Stop: 1bit | ::Stop: 1bit | ||
::Flow control: None | ::Flow control: None | ||
| − | :*Type AT command "AT+CGMR" and see the response on the console. | + | :*Type AT command "AT+CGMR" and see the response on the console. |
| + | |||
[[File:WISE-1570-FirstExample 03.png|center|300px|WISE-1570-FirstExample 03.png]] | [[File:WISE-1570-FirstExample 03.png|center|300px|WISE-1570-FirstExample 03.png]] | ||
| − | |||
Revision as of 11:41, 15 November 2018
Contents
Introduction
WISE-1570 Software Development Kit (SDK)
Setup Development Environment
Preparing for Hardware
- For mote, WISE-1570, WISE-1500 and WISE-ED22 or WISE-ED20.
- PC running LINUX operating systems such as Ubuntu 16.04.1.
Please refer to the following steps for setup a WISE series of boards before using WISE-1570 SDK.
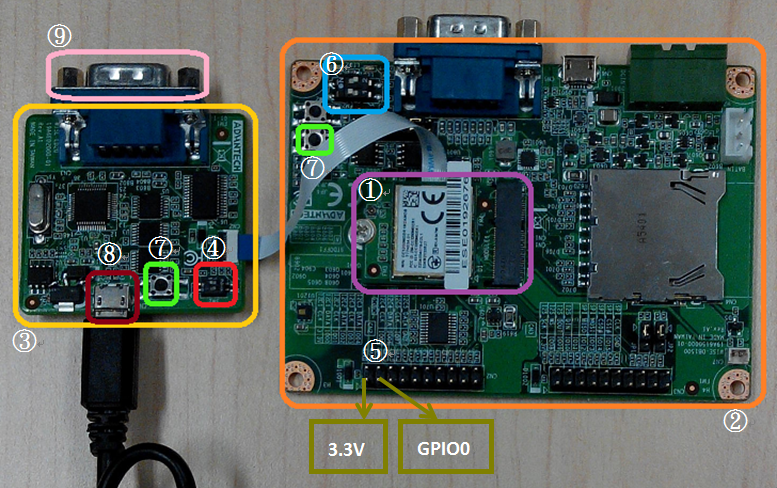
①WISE-1570
The user must to choose the CN1 on WISE-1570 as below is connected to WISE-ED20 or WISE-ED22 through FPC.
②WISE-1500
③WISE-ED20
④SW2 on WISE-ED20
- Please check pin1 and pin2 to “ON” as default.
- Switch pin1 to “ON”: flash programming, “OFF”: boot from flash.
⑤CN2 on WISE-1500
- Booting into the mode of network connection when both 3.3V and GPIO0 are opened.
- Booting into the mode of console of API when both 3.3V and GPIO0 are shorted.
⑥SW3 on WISE-1500
- Please check pin1 and pin2 to “OFF” as default.
- Switch pin2 to decide whether running “backup to default” while device booting. “ON”: enabled, “OFF”: disabled.
⑦One reset button on WISE-1500 and the other on WISE-ED20
⑧Micro USB connector
- Power supplies for UART3 debug port.
⑨Com port
- No supported.
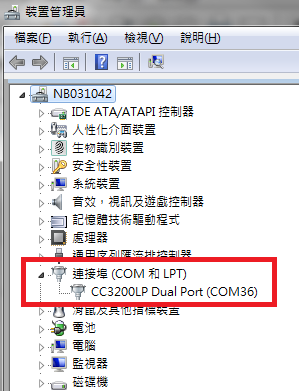
Step02: Connect the WISE-ED20 to PC using micro-USB cable.
The device will be visible in the Device Manager as below after FTDI driver installed. The user can find the FTDI driver in source tree.
ARM mbed
The ARM mbed is IoT device platform and it has a lot of resources for IoT development. We supported ARM mbed OS on WISE-1570 to make user easily to get started and obtain great benefit from ARM mbed.
mbed CLI
The mbed CLI is command-line tool. The user needs to setup CLI for WISE-1570 SDK and please follows the steps to install related tools. For more details, please refer to mbed CLI.
Note: We expected the user setups mbed CLI in Linux as default. If the user preferred Windows, ARM mbed provides the Video tutorial for manual installation.
- Install Python
- mbed CLI supports Windows, Linux and Mac OS X operating systems. You can select the OS you prefer to work with. mbed CLI is a Python script, so you’ll need Python to use it. The version 2.7.11 of Python has been verified with mbed CLI.
- Note: mbed CLI is incompatible with Python 3.
Install python 2.7.11 $ sudo wget https://www.python.org/ftp/python/2.7.11/Python-2.7.11.tgz $ tar zxvf Python-2.7.11.tgz $ cd Python-2.7.11 $ sudo ./configure $ sudo make altinstall Check the python version $ python --version
- (Optional) Install Git or Mercurial
- If you would like to maintain your source code in repositories, you can continue with the next step. mbed CLI supports both Git and Mercurial repositories, you can install which one you prefer:
- Git - version 1.9.5 or later.
- Mercurial - version 2.2.2 or later.
- If you don’t want to use repositories, you can just skip it.
Git install commands as follow
Install Git latest $ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:git-core/ppa $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install git Check the git version $ git --version
Mercurial install commands as follow
Install mercurial latest $ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:mercurial-ppa/releases $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install mercurial Check the mercurial version $ hg --version
- Install GCC
- mbed CLI invokes the mbed OS 5 tools for various features, such as compiling, testing and exporting to industry standard toolchains. To compile your code, you will need either a compiler or an IDE:
- Compilers: GCC ARM, ARM Compiler 5, IAR.
- IDE: Keil uVision, DS-5, IAR Workbench.
- We select GCC ARM Embedded, so you can install version 4.9 of GCC ARM Embedded.
Install GCC ARM Embedded $ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:team-gcc-arm-embedded/ppa $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install gcc-arm-embedded Check the Gcc version $ arm-none-eabi-gcc --version
- Note: When installing the Arm Compiler 5 on a 64-bit Linux machine, you may need to also install the i386 architecture package:
$ sudo dpkg --add-architecture i386 $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install libc6:i386 libncurses5:i386 libstdc++6:i386
- Install mbed CLI
- You can get the latest stable version of mbed CLI from PyPI
$ pip2 install mbed-cli
- Note: On Linux or Mac, you may need to run with sudo.
- Other necessary package
$ sudo pip2 install colorama $ sudo pip2 install pyserial $ sudo pip2 install prettytable $ sudo pip2 install jinja2 $ sudo pip2 install intelhex $ sudo pip2 install junit_xml $ sudo pip2 install mbed_ls $ sudo pip2 install beautifulsoup4 $ sudo pip2 install fuzzywuzzy $ sudo pip2 install mbed_host_tests $ sudo pip2 install mbed_greentea
mbed CLI configuration
- GCC_ARM_PATH
- Set GCC_ARM_PATH to the binary directory of your GCC Arm installation
$ mbed config -G GCC_ARM_PATH "/home/erick/gcc-arm-none-eabi-4_9-2015q3/bin" [mbed] /home/erick/gcc-arm-none-eabi-4_9-2015q3/bin now set as global GCC_ARM_PATH
Flash Programming
Programming through WISE-ED22
Please refer to WISE-ED22 for flash programming.
Software API
Mbed API
MQTT-SN API
Example
First Example
The user can use this example to communicate with RF by specified AT command. Please follow the below steps to give it a try. About AT command manual if needed, please get in touch your contact person from ADVANTECH.
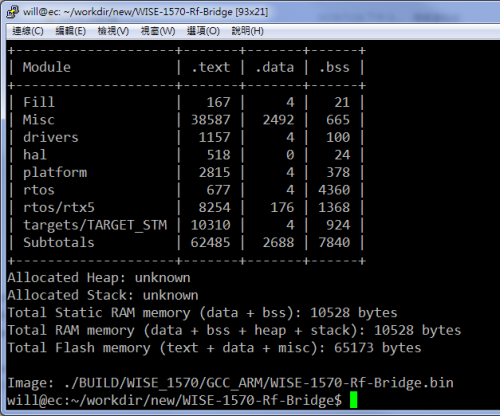
- Step01: Get source code and compile it by mbed CLI.
- Please click "Link to source" and review the file "README.md" to know how to deployment and compilation with this example. The output binary will be "source_dir/BUILD/WISE_1570/GCC_ARM/WISE-1570-Rf-Bridge.bin"
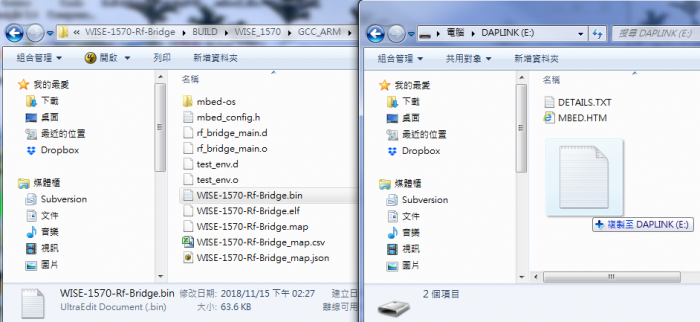
- Step02: Flash programming by WISE-ED22
- Check device connected from WISE-ED22 to PC using micro-USB cable and use drag-and-drop programming with your binary.
- Step03: Get the version of RF by AT command "AT+CGMR"
- Choose any terminal you like. (e.g., the snapshot is setting of Tera Term.)
- Please set terminal as the below setting:
- Baud rate: 9600
- Data: 8bit
- Parity: None
- Stop: 1bit
- Flow control: None
- Type AT command "AT+CGMR" and see the response on the console.
Peripheral
I2C
This example use I2C bus to read humidity and temperature sensor which is built-in WISE-1500
#include "mbed.h"
#define TI_HDC1050_DEVICE_ADDR 0X40
#define TI_HDC1050_TEMPERATURE_ADDR 0X00
#define TI_HDC1050_HUMIDITY_ADDR 0X01
#define TI_HDC1050_CONFIGURATION_ADDR 0x02
#define TI_HDC1050_SERIALID0_ADDR 0XFB
#define TI_HDC1050_SERIALID1_ADDR 0XFC
#define TI_HDC1050_MANUFACTURER_ID_ADDR 0xFE
#define TI_HDC1050_DEVICE_ID_ADDR 0XFF
#define TI_HDC1050_MANUFACTURER_ID 0x5449
#define TI_HDC1050_DEVICE_ID 0x1050
static I2C i2c0(I2C0_SDA,I2C0_SCL);
static DigitalOut g_tPower(CB_PWR_ON);
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
char rxBuff[4];
char ofs = TI_HDC1050_TEMPERATURE_ADDR;
uint16_t u16Humidity = 0;
float fTemperature = 0;
I2C *i2c = &i2c0;
g_tPower = 1;
//
// Set clock frequency of I2C interface is 100KHz
//
i2c->frequency(100000);
//
// Access sensor by read/write transaction through I2C interface
//
for(int i=0; i<10; i++) {
i2c->write(TI_HDC1050_DEVICE_ADDR << 1, &ofs, 1);
wait_ms(100);
i2c->read(TI_HDC1050_DEVICE_ADDR << 1, rxBuff, 4);
fTemperature = (float)(( rxBuff[0] << 8) | (rxBuff[1] ));
fTemperature = (fTemperature*165)/65536-40;
u16Humidity = (rxBuff[2] << 8) | (rxBuff[3] );
u16Humidity = (u16Humidity*100)/65536;
printf("temperature:%.2f, humidity:%d \n\r", fTemperature, u16Humidity);
wait(1);
}
return 0;
}